Yaska and Panini – Part One
YASKA
Yaska and Panini are two of the most celebrated scholars of the Sanskrit linguistic sciences. Yaskacharya is renowned as a Great Etymologist (Niruktakara), whose work, the Nirukta, is looked upon as the oldest available authoritative treatise concerning derivation of certain selected Vedic words. And, Panini, the Grammarian par excellence (Maha-Vaiyakaranah), is reverently addressed as Bhagavataḥ Pāṇineḥ Acārya. And, his Grammar Aṣṭādhyāyī (Pāṇinīkṛta–Sūtrapāṭham), the most distinguished treatise that set the linguistic standards for Classical Sanskrit, is referred to as Paniniyam Maha-shastram.
There is often a tendency to compare the approach and the methods adopted by the two Greats to their respective fields of study.

It is said; Yaska preceded Panini (Ca.5th century B C E) by about a century or, perhaps, more. This is based, rather tentatively, upon the Sutra: Yaska-adibhyo gotre (PS_2.4.63) in Panini’s Astadhyayi. Further, Patanjali, the author of Mahabhashya on Panini’s Astadhyayi, suggests that Yaska hailed from the Paraskara Country – (pāraskaraḥ deśaḥ – P_6, 1.157) – (?*), on the basis of Panini’s Sutra – Pāraskara-prabhṛtīni ca saṃjñāyām (PS. 6.1.157). And often, salutations are submitted to Yaska with the mantra: Namo Paraskaraya, Namo Yaskaya.
[*According to some,Paraskara corresponds to Tharaparkar in the Sindh region]
It appears during the time of Yaska, the then contemporary Sanskrit, though not the same, was yet somewhat near to the Sanskrit of the ancient Vedas (Chhandas). In fact, Yaska, in his Nirukta (1.1; 1.15), remarks: the Vedic stanzas are still meaningful; because, their words are almost close to the currently spoken Sanskrit. However, understanding certain obscure terms of Vedic Mantras had become rather difficult.
samāmnāyaḥ samāmnātaḥ sa vyākhyātavyaḥ /1.1/.. Atha api idam antareṇa mantreṣv artha pratyayona vidyate / Nir.1.15 /
The Sanskrit, when it was a living language, was evolving and changing from period to period. For instance; the language of the Upanishads is not, in every respect, the same as the language of the Rig-Veda. And again, the language of Classical period differed, substantially, from that of the Upanishads. Apart from that, the Sanskrit of the Buddhist texts of Tibet , Nepal and Northern India followed a slightly different Grammar.
Accordingly, by the time of Yaska, the Sanskrit language had changed a great deal since the period of the Vedas; and, was more or less bereft of the characteristic Vedic phonetic and semantic forms. But, at the same time, the link between the Vedic idioms and the contemporary language had not entirely worn-out.
Nevertheless, in the process, over a period, say by the First millennium BCE, interpretation of certain Vedic terms had indeed become rather vague and imprecise. The tradition had apparently broken down; and, by the time of Yaska, the meaning of some archaic words in the Vedic Riks could no longer be grasped clearly.
Yaska points out the differences between the Vedic Sanskrit (which Panini calls as Chhandas) and the contemporary language (Bhasha)
– Na iti pratiṣedha arthīyo bhāṣāyām ubhayam anvadhyāyam (Nir.1, 4)
Yaska described the position then obtaining (Nir.1.20); and, remarked: the Rishis, who envisioned, had direct perception (dṛṣṭayo bhavanti) of the meaning of the Vedic hymns (evam ucca avacair abhiprāyair ṛsīnām mantra dṛṣṭayo bhavanti –Nir.7.3). But, the later generations had lost that faculty; and, did not fully understand the meaning of certain mantras. Therefore, with a view to helping the future learners in comprehending the meaning of certain difficult passages of the Vedas, the texts like Nighantu and Nirukta were composed.
Upadeśāya glāyanto avare bilma grahanāya imam grantham samāmnāsiṣur vedaṃś ca veda aṅgāni ca- // Nir.1.20 //
**
Yaskacharya believed that every Vedic word has an expressive power to denote a certain sense. And, as a signifier (vacaka), every word is eternal (vyaptimattvat tu sabdasya – Nir.I.2); and, it performs a critical function in helping to arrive at an unerring, definitive meaning of a statement.
Yaska, therefore, remarks that it is essential that one should realize this truth. And, in the absence of such realization, a person, who merely recites the Vedas, without comprehending its meaning, would be like a pillar (sthaanu) or a mere load-bearer (bhara-haara). And, it is only he, who fully grasps and appreciates the meaning of what he is reciting (arthajña), that will attain the good – both here and hereafter (sakalam bhadram-aśnute-nākam); having been purged of all impurities by the power of knowledge (jñāna vidhūta pāpmā).
sthāṇur ayam bhāra-hāraḥ kila abhūd adhītya vedam na vijānāti yo artham / yo arthajña it sakalam bhadram aśnute nākam eti jñāna vidhūta pāpmā (Nir.1. 18)
Yaska goes further; and tenders a sage-like counsel (Nir.1.18): what is taken from teacher’s mouth, but not understood and, is merely repeated, never flares up. It is like dry firewood flung on something that is not fire.
Don’t memorize, seek the meaning / What has been taken [from the teacher’s mouth] but not understood/ Is uttered by mere memory recitation / It never flares up, like dry firewood without fire / Many a one, although seeing, do not see her / Many a one, although hearing, do not hear her/ And for many a one, she spreads out [Her] body, like a wife desiring her husband. / The meaning of Speech (Vac) is its fruit and flower. (Translation by Eivind Kahrs)
Yad gṛhītam avijñāta nigadena eva śabdyate/ anagnāv iva śuṣka edho na taj jvalatikarhicit/ sthāṇus tiṣṭhater artho arter araṇastho vā / Nir. 1.18 /

Nighantu
As mentioned earlier, in order to instruct , to guide and to help such of those who were ill at ease with the Vedic language; and, those who did not fully comprehend the meaning of the mantras, the texts such as Nighantu (joined together or strung together words) and others were compiled; its plural being Nighantava. Yaska calls these texts as Samāmnāyam Nighaṇṭava (enumerations) –Nir. 1, 1
[Albrecht Weber (The History of Indian Literature (1892) on page 25) points out that correct name of such texts should be Nigranthu (strung together); and, not Nighantu, as it is generally called]
The Nighantu could briefly be described as a glossary of certain Vedic words – in the exact form in which they appear in the Vedic texts; and, as the earliest known systematic work, clearly dividing the words of the Sanskrit language into the groups of nouns, verbs , prepositions and particles.
[However, Nighantu is not an exhaustive list of all Vedic words. It includes only such words as were considered ambiguous, obscure, or synonymous.]
Durga , the commentator, therefore, calls Nighantu an example (Udaharana); and, he explains its purpose by saying : In order that we get the knowledge of the meaning of the Vedic verses (mantra-artha-parijnana), the Rishis have composed (sam-amnaya) this text, which in its five parts (pancha-adhyayayi), could serve as an example for forming a more exhaustive compendium of the Shastras.
Sa Ca Rsibhir mantra-artha-parijnanayo udaharana bhutah, pancha-adhyayayi shastra samgraha bhaven ekasmin amnaye granthikrta ity arthah (1.30;3-4)
*
The Nighantus, as a class of texts, consist five chapters, which are again divided into three sections.
The first section, comprising the first three chapters, deals mainly with synonyms (Nighantuka-kanda), which, perhaps, is the earliest.
The second section covering the fourth chapter (Naigama or Aikapadika-kanda) dealing with homonyms, contains a list of ambiguous and particularly difficult words of the Veda.
The third section, covering the fifth chapter (Daivata-kanda), gives the names of deities; and, their classification under the three regions, earth, sky and the intermediate space.
The Nighantus, upon which Yaska offers his comments, are the most ancient in a long and hoary tradition of lexicography. Besides the Nighantus and the Nirukta there are the Koshas (vocabularies) and Anukramanika (indexes).
The Nighantu, which mostly lists the archaic words occurring in the Rig-Veda, is also meant to functions as a compliment to the Vyakarana (Grammar).
In addition, it also serves a practical purpose; which is to help and guide the Yajnaka (the one who performs the Yajnas), in unerringly identifying the Devata of a mantra, so that the Yajna is performed well, without a blemish; and, its objective is achieved successfully.
[ Émilie Aussant , Univ. Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Paris, France, writes in her Linguistics in Premodern India
Classical Sanskrit lexicography (Kosa) played an important role in Indian scholarship, especially poetry: the aim of classical lexica, which were learnt by heart, was to help poets in composition, where synonyms of varying syllable structure are required to satisfy metrical constraints.
Two main kinds of lexicon (Kosa) were composed: synonymic (Ekartha, Samanartha) ; and where words are classified according to subject (e.g. words relative to heaven, sky, time, thought, sound, etc.); and homonymic (Anekartha, Nana-artha) , which list words having more than one meaning .
Sanskrit poetics (Alamkara) is an erudite discipline that accompanied Sanskrit literary production (mainly, Kavya) , the refined poetry) for nearly two millennia. It addressed, among other questions, the following issues: analysis of the formal, logical, semantic and pragmatic aspects of simile and other tropes; word classes; word meanings (denotation, metaphor, suggestion); sentences, passages ; and, whole literary works’ meanings, language registers.]
*
Nirvachana
Further, with a view to comprehend and to restore the correct meaning of certain antiquated words appearing in the Vedas, the method of Nirvachana (Nir+Vac = clear explanation of words) was applied to the glossary of Nighantu.
The term Nirvachana, which embodies the principles of etymology, is understood as the study which enables the analysis of a word; its formation; the different senses it conveys (yathartham), in accordance with its derivation (vyutpattih) — (Nirvachanam nama sabdasya yathartham vyutpattih); and, by taking into account the contextual factors (samsarga) , as well.
Such a field of analytical study had perhaps become necessary; because, almost a quarter of words in the Vedic texts, composed in the Second millennium BCE, appeared just once; and, their meaning and intent had become imprecise.

Nighantu -Nirukta
The related field of learning, which deals with the derivation and semantic explanation of words, came to be known as Nirvachana Shastra or Nirukti, (‘interpretation’ or derivation and semantic explanation of words) a branch of etymology.
It attempted to systematically put forward theories on how words are formed; and, how their meanings are to be determined in the context of the Vedas. Its related subsidiary texts were known as Nirukta (Nir + Ukta or Nir-Vac = to state or to explain clearly).
And, Nirukta developed into a branch of etymology; offering explanations about the derivation of certain chosen words of the Vedas , in order to comprehend; to determine; and, to restore their proper meaning. In the process, the Nirukta systematically discussed how to understand the significance of archaic, uncommon words used, mainly, in the Rig-Veda.
Nirukta is very closely connected with the Vedas. The body of Yäska’s work is a commentary on most of the words of the Nighantu; which again is a glossary of certain Vedic words. The main task of the Nirukta of Yaska is to explain most of the rare and obscure Vedic words by resorting to various possible etymologies.
[Sri Sayanacharya , in the preface to his Rig-bhashya, extols the approach of Yaska for explaining the uncommon aspects (Tattvas) of the Vedas; while other Vedangas are engaged in secular subjects
– arthāvabodhe nirapekṣatayā padajātaṃ yatroktaṃ tan Niruktam
Sri Sayana concluded his exposition of the Nirvachana-shastra with the remark: the Nirukta is useful for grasping the meaning (Artha) of the Vedas
– tasmat Veda-rtha ava bodha- upayuktam Niruktam ]

The Brahmana texts
It is said; the Brahmana texts were indeed the earliest attempts made in the study of etymology (Nirukta) of Vedic words.
The etymologies in the Bråhmanas were believed to bring to light the connections that underlie between the explicit and the implicit ideas that are normally concealed. Such revelations also helped to emphasize the fact that words could, often, have multiple etymologies.
And, with that, it was realized that certain words may possibly have the potential to function as the network of ideas; not being confined to merely suggesting the possibility of having a set of synonyms’.
It is said; the Brahmana texts explain the mantra-passages in ten different ways –Nirvachana; and Vyava-dharana-kalpa.
The advantages of analyzing a word or a technical term; and studying it from the point of view of more than one etymology, are said to be, that one gains access to the realities that were till then latent or hidden. Which is to say; one becomes aware of the unknown through the known. The knowledge, so acquired through such revelation – the texts emphasize repeatedly – are of great importance: as, it helps to widen the awareness of one who is fired with zeal to learn.
And, Yaska’s work, as also the works of those other Nairuktas, who preceded him, such as Sakapuni, Aupamanyava, et al, were all said to be based upon the derivations and explanations as provided in the Brahmana literature. That is evidenced by the fact that all the characteristic features of the etymologies in the Nirukta are said to be based in the Bråhmanas. And, the Brähmanas many times provide the narrative background for an etymology given in the Nirukta. Further, Yaska also frequently quotes passages from Brahmana-texts, in support of his etymologies.
Some scholars regard Yaska’s Nirukta as a methodical extension of the explanations of words, as in the Brähmanas.

Yaska’s Nirukta
Yaska’s Nirukta brings together and presents, with comments, in a cohesive form those matters that were already discussed in other earlier texts. And, the selected Verses of the Rig-Veda, of course, are the main substance that is commented upon and made explicit, by using illustrative passages and the explanations as given in the Nighantu and in the Brahmanas. And, this forms the important part of Yaska’s Nirukta.
Nirukta as a distinct branch of etymology is primarily concerned with the meaning of a word or of a term – Artha pradhana; and, determines the meaning it conveys or is intending to convey, by tracing the roots of its formation.
Sri Sayana gives an analysis of the name of Yaska’s Nirukta: that which fully (nihsesha) provides (ucyante) the various possible (sambhavitah) meanings of the constituent elements (avayava-artha) of each individual word (ekaikasya padasya) by tracing its root (vyutpatti), is called Nirukta.
Tad api Niruktam ity ucyate / ekaikasya padasya sambhavita avayav-arthas tarta nihseseno ucyante iti vyutpatteh /
Here, the context in which the word appears, as well as the function it serves therein, assumes much importance, in order to understand the real significance of a word. Because, the Nirvachana principle, which is adopted in the Nirukta is , essentially, concerned with the formation of a word , and meaning in a given context; and , in a different context, the word could give forth a different meaning; then, the Nirvacana would also differ.
evam.anyesām.api.sattvānām.saṃdehā.vidyante/tāni.cet.samāna.karmāṇi.samāna. Nirvacanāni –Nir. 2, 7
It is therefore, said; a Niruktakara would never handle a word, torn out of its context (Na ekapadani Nirbhuyat- Nir.2.3); because, it would otherwise lead to a mere speculation about its probable intended meaning.
[Similarly, Bhartrhari clarifies (VP.1.59): all the elements extracted from the word in the course of linguistic analysis are valid in their own context. The elements that are relevant in the context of one activity may not be valid in the context of another. That is to say; each kind of activity, i.e. each kind of communicative situation, has its own reality , which in some ways might differ from the realities of other situations.
bhedenāvagṛhītau dvau śabdadharmāv apoddhṛtau/ bhedakāryeṣu hetutvam avirodhena gacchataḥ (VP.1.59) ]
*
Yaska’s Nirukta is not a ‘basic text’ of a Nirvacana-shastra from which a certain tradition of interpretation distinct from Vyakarana develops. It is, initially, a commentary on the Nighantu texts, which, again is a glossary of Vedic words; and, subsequently, it is an explanation of certain selected passages from the Rig-Veda. Thus, the two traditions – Vedic and Nighantu- are intertwined in Yaska’s work.
According to Yaska, every Vedic word has a meaning; and, denotes an appropriate sense. A mantra, for the Nirukta, suggests the activity of the mind (mantro-mananath). Here, speech is regarded as the vehicle of thought; and, whatever that comes within the purview of thought also comes within the purview of speech. In other words; Nirukta belongs to class of texts that are designed to intellectually explore and present the precise meaning of the Vedic mantras.
The aim of Yaska’s etymology is to understand the real significance of a word. It is not a subject of antiquarian interest; but, is of great importance to the study of meaning of Vedic mantras by countless generations that succeeded Yaska.
Besides that, the etymology featured in the Nirukta is of great importance for the study of Sanskrit language, in general. Patanjali, in his Mahabhashya, very frequently refers to Yaska’s Nirukta; and, so does Sri Sayanacharya , in the later times.
Nirukta is important for several other reasons, as well. Firstly, it presents the type of the earliest classical style that was used in the Rig-Veda; and, secondly, it is the oldest known attempt in the field of Vedic etymology.
As regards the importance of the etymology, the Nirukta, Yaska asserts , right at the commencement of his work : without this science, one cannot gain the precise meaning of certain Vedic terms; and , therefore, one cannot clearly understand and grasp of the import of Vedic mantras, as well.
Samāmnāyah samāmnātaḥ sa vyākhyātavyaḥ / idam antareṇa mantre ṣvra artha pratyayo na vidyate iti – Nir. 1,1
[ Please do not fail to read the remarkable study on the Language of the Nirukta by Dr. Mantrini Prasad (DK Publishing House – 1975). It is very thorough, detailed and authoritative; and, is imperative for anyone earnestly undertaking the study of Yaska’s Nirukta.]

Word (Sabda) and Meaning (Artha)
Yaska uses the term Sabda to denote ’the word’ as also ‘the sound’. The sound could either be (a) inarticulate (various natural sounds) – dhvanya-tmaka; or (b) articulate – varnat-maka
The articulate sounds (varnat-maka sabda) can be comprehended by the listeners without much effort
– (Vyāptimattvāt tu śabdasya aṇīyastvāc ca śabdena sañjñā karaṇa vyavahāra artham loke – Nir.I.2) .
And, it again, has two forms (i) Sarthaka (meaningful); and (ii) Anarthaka (meaningless).
Here, Yaska mentions about the meaningless particles (Nipata) used as expletives ; such as : kam, im, id and u (Nir.I.9) – nipātā ucca avaceṣv artheṣu nipatanti (Nir.1.4).
Yaska’s list contains 23 Nipatas ; and, additional two Nipatas (total being 25)
Atha ye pravrtte arthe amita aksaresu granthesu vākya pūranā āgacchanti pada pūranās te mita akṣareṣv anarthakāh kam īm id v iti (Nir.I.9).
He has discussed, at length, about the words which are formed from the articulate (varnat-maka), natural, meaningful sounds, (Sarthaka).
It is said; the word (Pada) is the signifier (Vacaka); and, the meaning (Padartha) that is signified is (Vachya). That relation – Vacya-vacaka bhava – is determined by the primary function or Abhidha of a word. And, the essence of a word lies in its denotative or expressive power (Shakti).

Nirukta –Vedanga-Vyakarana
In the linguistic traditions of ancient India, Vyakarana, of course, occupied a preeminent position. But, at the same time, the value of a parallel system of linguistic analysis – Nirvachana shastra or Nirukta – which served a different purpose – was also well recognized.
Both these traditions are classed among the six Vedangas, the disciplines or branches of knowledge, which are auxiliary to the study of Vedas; and, which are designed to preserve and to carry forward the Vedas to the succeeding generations, in their pristine purity.
As said earlier; the Nirukta is reckoned as one among the six Vedangas, the ancillary Vedic sciences or disciplines related to the study of Vedas; the other five being: Vyakarana, Shiksha, Chhandas, Kalpa and Jyotisha.
Of these, the study of Nirukta is closely related to Vyakarana (Grammar). The Nirukta and Vyakarana are unique to each Veda; whereas, the other Vedangas – Shiksha, Chhandas, Kalpa and Jyotisha – are common for all Vedas.
Though, the study of Nirukta is associated with one of the Vedangas viz., Vyakarana (Grammar), each of the two has its own focus. And, though they are divergent, they also overlap in certain areas.

As mentioned, the main task of the Nirukta of Yaska is to explain most of the rare and obscure Vedic words, by way of pointing out various possible etymologies.
Here, his Nirukta focuses on linguistic analysis to help establish the proper meaning of the words, given the context they are used in the Vedic texts. In such etymological explanations, Yaska has stressed on the meaning of the word (Artha nitya parīkṣeta kenacid vṛtti sāmānyena- Nir.2.1), than its grammatical modifications.
Further, Yaska’s work is, culturally and intellectually, closer to the Samhitäs and Brähmanas, as compared to the Astadhyayi of Pänini.
The scope of Vyakarana, the Grammar, is much wider than that of the Nirukta; and, it covers all formats of the language. For instance; Panini discusses both the Vedic language (Chhandas) as also the bhäsä, the contemporary language, in general, spoken by the well-educated.
The term Vyakarana is defined as: Vyakriyate anena iti Vyakarana – Grammar is that which enables us to form and to examine words and sentences; and, it is both that which is to be described (lakshya) and the means of description (lakshana).
Patanjali explains; that which is to be described is the word (sabda); and the means of description is the rule (Sutra),consisting of general and specific statements .
A Grammarian determines the meaning of a word by tracing the process of its formation.
An etymologist determines the formation of a word by tracing the meaning it conveys or desires to convey.
Durga, the commentator, remarks: the Grammar (Vyakaranam) is an independent (svatantram) precise and logical system of knowledge (vidyasthanam). It deals with linguistic analysis – Lakshana pradhana – to establish the exact form of words to properly express ideas. For that purpose, it lays down the general and specific rules, which enable us to understand the exact meaning of the words (artha-nirvacanam).
Svatantram e vedam vidyasthanam artha-nirvacanam Vyakaranam tu laksana-pradhanam
And, Nirukta is the explanation of the meanings; it focuses on linguistic analysis in order to help establishing the proper meaning of the words, given the context they are used in the Vedic texts.
*
And yet, the Nirukta complements the study of Vyakarana; since, it explains the words that are not analyzed by the Vykarana. And at the same time, it accomplishes its own purpose, which is to provide a clear understanding of the portions of the Rig-Veda text it commented upon.
Yaska asserts that the prerequisite to the study of Nirukta is the proper learning of Vyakarana. (Grammar) * .
[*But, at the same time, Yaska remarks: while deriving the meaning of a word, in its own context, one should try to stick to the rules of the Grammar (Vyakarana) as far as possible; but, if this is of no avail in bringing out the hidden meaning of the term in question, then one should abandon such rules
– na saṃskāram ādriyeta / viśaya-hi vṛttayo bhavanti (Nir.2.1)]
*
Thus, the Nirukta, as a class of texts, is intimately related to several branches of studies, such as: the Vedas; the Brahmanas; the Nighantu; as also to the Grammar (Vyakarana) in general.

Niruktas of the pre-Yaska period
Yaska recounts the several Schools of Grammar or the Grammarians who flourished before his time : Agrayana; Aindra; Apisali; Aupamanyava; Aurnabhava ; Chakravarmaṇa; Galava ; Gargya; Kashyapa ;Kaṣakṛtsna ; Katthakya ; Kautsa Kraustuki; Kuṇaravaḍava ; Sakalya; Sakaṭayana; Senaka ;Shakapuni; Sphoṭayana and others.
And, it appears; by about seventh or sixth century BCE, many of these Grammarians had compiled Nirukta texts. But, sadly, all those earlier versions of Niruktas disappeared gradually in the course of time. It is only the Nirukta that was composed by Yaska that has survived; and, has come down to us.
Yaska, in his own Nirukta, refers to the views (either in his support or to show their divergence) that were offered by as many as sixteen compilers (Nirukta-karas) of the Nirukta class of texts that were in existence and in circulation prior to his time (Ca. 6th century BCE) .
[Hartmut Scharfe in his Grammatical Literature remarks : one of the interesting parts of the Nirukta is that it gives us more information on early Grammarians than any other source. And, it is all the more valuable, since almost all other information on Pre-Paninian Grammarians in the later literature is rather suspect.
In course of his work, Yaska mentions twenty four great teachers and seven different schools by name; in addition to referring to some others in a general way]
-
-
- (1)Agrayana (1.9; 6.13;10.8);
- (2) Audumbarayana (1.1);
- (3) Aupamanyava (1.1; 2.2; 2.5; 2.11; 3.8; 3.11; 2.19; 5.7; 6.30; and, 10.8);
- (4) Aurnavabha (2.26; 6.13; 7.1; 12.1; and, 12.19) ;
- (5) Katthayaka (8.5; 8.6; 8.17; 8.10; 9.41; and, 9.42);
- (6) Kusta (1.15);
- (7) Kraustuki (8.2);
- (8) Gargya (1.3; 1.12; and,1.25);
- (9) Galava (4.3);
- (10) Karmasiras (3.15);
- (11) Taitiki ( 4.3 ; 5.27 );
- (12) Varshyayani (1.2);
- (13) Satabalaksa Maudgalya (9.6);
- (14) Sakatayana (1.12; 1.13);
- (15) Sakapuni (Nir.3.11 ;3.13 ;3.19; 8; 4.15; 5.3 ; 5.28; 7.14; 7.28; 8.5; 8.6; 8.10; 8.12; 8.14; 8.17; and, 12.40); and,
- (16) Sthaulashtivi (7.14; 10.1).
Source: http://ignca.gov.in/Asi_data/16247.pdf (pages 62 to 90) , of Sri Bishnupada Bhattacharya ‘s scholarly work Yaska’s Nirukta and the science of etymology (1958)]
Of the many such Nirukta-karas; Yaska, in his Nirukta, frequently cites the explanations provided by Aupamanyava; Aurnavabha; and, Katthayaka. But, Sakapuni Rathitara is the most frequently quoted Nirukta- teacher. His views are cited by Yaska as many as about twenty times.
It is believed; each of the Nirukta-karas, who preceded Yaska, had his own Nighantu text. And, perhaps, Yaska too had his own Nighantu.
But, such works – Nighantus as also Niruktas – of all those savants, who preceded Yaska, are lost. And, it is only the Nirukta of Yascacharya that has stood the test of time for over two thousand seven hundred years; and, is acclaimed, for its excellence, as the most authoritative text in its class.

Manifold approaches to the study of Vedas
There are several approaches or methods that are generally applied for the systematic study, analysis and interpretations of the Samhita texts (the Vedas). Yaska also recognized that the Vedic texts presented multiple aspects; and could be studied and interpreted in various different ways.
Accordingly, the Samhitas were analyzed and interpreted, in varied ways, by earlier authors adhering to different sets of disciplines , such as: Yajnika (ritualists); Nairuktas (etymologists); Aithihasika (those who traced the historical traditions); Naidana (mix of history and etymology); Parivrajaka (ascetics); the Dharma-shastrika (those who interpreted books of moral code and conduct); and, the Vaiyakaranas (Grammarians)
– Aitihasikah, Nairuktah, Naidanah, Parivrajakah, Yajnikah, Dharma-shastrika and Vaiyakaranah.
:- The Yajnika-s, whose primary interest was the performance of the Yajna, were more concerned wiith the sequence of the rituals to be conducted during the course of the Yajna; and, the proper utterance of the related Vedic mantras; than with the meaning of the mantras that were recited by them.
tatra etad yājñikā vedayante triṃśad uktha pātrāni mādhyandine savana eka devatāni tāny etasmin kāla ekena pratidhānena pibanti tāny atra sara ucyante/ 5.1/
:- The Aithihasikas, on the other hand, try to relate a hymn or a Vedic passage to an event or an account concerning a deity, as narrated in a mythical story. (This, of course, is totally different from the historical analysis of the present-day.) – tvāstro.asura.ity.aitihāsikā / 2,16 /
:- The Naidanas’ (said to be specialists on the theory of causation) approach was similar to that of Aithihasikas – ṛcā samaṃ menaḥ iti naidānāḥ ।
:- The Parivrajaka, the wandering philosophers, Adhyatma-pravada, try to interpret almost every aspect of a Samhita text in terms of spiritual or mystical context- bahu.prajāḥ.kṛcchram.āpadyata.iti.parivrājakā 2,8
:- The Dharma-shastrikas search for points of Law or precedence in the accounts narrated in the Vedas – sākṣāt.kṛta.dharmāṇa.ṛṣayo.babhūvuḥ / te. avarebhyo. asākṣāt. kṛta. dharmabhya. upadeśena.mantrānt.samprāduḥ /1,20 /
:- The Vaiyakaranah, the Grammarians are mostly interested in the linguistic analysis of the Vedic texts – mandayater.iti.vaiyākaraṇāh / 9,5 /
But, Gargya remarks : Not all , only some Grammarians — Na sarvani iti Gargyah vaiyyakarananam ca eke syath
*
In contrast, Yaska chose to adopt the method of Nirukta, which analyzes the words used in the Vedic mantras; and determines their precise meaning (Nirvachana) in their proper context.
Some scholars regard Yaska’s Nirukta as not only a work on etymology; but, also as a work on the most fascinating branches of philology, the study of language in oral and written historical sources.
But, the type of etymologies that Yaska adopted, does not typically establish a link with the mythological or historical realm; nor does it, as a rule, reveal hidden layers of language.
It is explained; such a semantic etymology is to be distinguished from a historical etymology.
A historical etymology presents the origin or the early history of a word in question. It tells us; for example, how a word in a modern language is derived from another word belonging to an earlier language, or to an earlier stage of the same language.
A Semantic etymology does something quite different. It attempts to connect one word with one or more others which are believed to elucidate its meaning. The semantic etymologies tell us nothing about the history of a word, but something about its meaning in a particular context.
[Dr.Saroja Bhate remarks: though some scholars interpret the term Nirvachana to mean Etymology, it is, in fact, different from the modern concept of Etymology. Yaska’s etymologies do not attempt historical analysis of words.]
In his remarkable work Nirukta, which also serves as a commentary on the Nighantu, Yaska attempts to establish the proper meaning of certain selected Vedic words, in the context of ‘how, where, when and why’ it is stated in the text .
Thus, the essential feature of Yaska’s commentary is the semantic interpretation of words based on their derivation (Nirvachana).
[As Peter M. Scharf explains in The Oxford Handbook of the History of Linguistics (11,2) : at times; Yaska provides a familiar synonym for an obscure word, in addition to its etymological derivation. For instance; in vayāḥ śākhā veteḥ (Nirukta 1.4) – the obscure word Vayāḥ is explained through a familiar word śākhā (the branches) ; and, Yaska says that vayāḥ is derived from the root vī (to move).
But, some etymologies in the Nirukta are less explicit; they utilize semantic statements from which a phonetic analysis is easily inferred. For instance; Nirukta 2.14 explains the six words contained in Nighaṇṭu 1.4.
svar ādityo bhavati. su araṇaḥ. su īraṇaḥ. svṛtaḥ rasān. svṛtaḥ bhāsam jyotiṣām. svṛtaḥ bhāseti vā.
The first, svar, is explained as follows by Sarup (1920–27: part II, p. 30):
Svar means the sun; it is very distant, it disperses (the darkness); it penetrates the fluids; it is luminary; its light penetrates or pierces through the objects. It is said; the term Svar can be derived from the pre-verb su plus the word araṇa ‘distant,’ īr ‘set in motion,’ or the root ṛ ‘go.’ The word araṇa is itself a derivation from the verb ṛ ‘go.’ ]
***
As Johannes Bronkhorst observes in his Etymology and magic: Yāska’s Nirukta, Plato’s Cratylus, and the riddle of semantic etymologies :
One way to account for the validity of such semantic etymologies based on the similarity between words (for those who accept this validity) would be to claim that there are ultimate meaning bearers, such as individual sounds or small groups of them, each with its own specific meaning
[For instance; as per its etymology, the term Indra denotes the one who, by his power (Indriya), energises or kindles the vital airs (prana). The Satapatha Bråhmana 6.1.1.2 says, since he kindled (indh), he is the kindler (indha ). But, cryptically, he is called Indra
sa yo yam madhye prāṇaḥ | eṣa evendrastāneṣa prāṇānmaindra ityācakṣate paro
‘kṣam paro ‘kṣakāmā hi devāsta iddhāḥ sapta nānā puruṣānasṛjanta – 6.1.1.[2]
Besides the etymology of Indra, as above (from Indh), the Taittiriya Bråhmana (2.2.10.4) offers an altogether different explanation: “No one can withstand this power (idam indriyam) in him; and, that is why he is called ‘Indra’.”
Different etymologies of one and the same word (often a name) are frequently met with, sometimes even in one and the same text. For instance;
The two different etymologies of the word Indra occur in one and the same passage at Satapatha Bråhmana 11.1.6.7
So’rcañcrāmyaṃścacāra prajākāmaḥ sa ātmanyeva prajātimadhatta sa āsyenaiva
devānasṛjata te devā divamabhipadyā sṛjyanta taddevānāṃ devatvaṃ yad divamabhipadyā sṛjyanta tasmai sasṛjānāya divevāsa tadveva devānāṃ devatvaṃ yadasmai sasṛjānāya divevāsa – 1.1.6.[7] ]

[According to Prof. Jan E.M. Houben, this is what Yaska said about the methodology that he adopted in the Second Chapter of his Nirukta, commencing with – Atha Nirvachanam, which states the characteristic features of Nirvachana.
– Artha-nirvachanam
With reference to this, the words, the accent and the grammatical form of which are regular and accompanied by a radical modification which gives a hint, should be derived in the ordinary manner.
But, If the meaning is not perspicuous; and, if there is no radical modification which gives a hint, one should investigate [the word to be explained], taking one’s stand on the meaning, according to a similarity (of a verbal root with a suitable meaning) – (Sama-artha-svara-samskara)- to the derived from (i.e., to the word to be explained).
Even If no similar [verbal root] is found, one should explain [the word] according to a similarity in syllable or phoneme – (Arthanityah parkseta kenchid vrtti samanyena)
But, never should one abstain from explaining [by deriving it from some root], one should not be attached to the grammatical form [too much], for the derived forms (i.e., the words to be explained) are full of uncertainties
Nir.2,1:atha.nirvacanam : tad.yeṣu.padeṣu.svara.saṃskārau.samarthau.prādeśikena.vikāreṇa(guṇena.Bh).anvitau.syātām.tathā.tāni.nirbrūyād;atha.ananvite.arthe.aprādeśike.vikāre.artha.nityaḥparīkṣeta.kenacid.vṛtti.sāmānyena;avidyamāne.sāmānye.apy.akṣara.varṇa.sāmānyān.nirbrūyān.na.tv.eva.na.nirbrūyāt;na.saṃskāram.ādriyeta.viśayavatyo.(hi.Bh).vṛttayo.bhavanti ]

Yaska’s Nirukta -structure
As mentioned earlier, Nirukta is the systematic creation of a glossary; written in archaic Sanskrit prose, which discusses how to understand antiquated, uncommon words used mainly in the Rig-Veda.
For the purpose of his study, Yaska chose about 600 stanzas from the Rig-Veda; and, created a well organized vocabulary to understand the meaning; and, to interpret, particularly, the archaic, uncommon words used in the Vedic texts (artha nityaḥ parīkṣeta kenacid vṛtti sāmānyena– Nir.2.1).
But, all the Mantras that he quotes are not fully explained by him. Often, Yaska passes past some mantras by saying: this mantra is self-explanatory – iti.sā.nigada.vyākhyātā (Nir.6.5). It is said; there are about 13-14 such mantras.
[Although, Yaska’s Nirukta hardly needs a commentary, in the later times, many commentaries came to be written. Of these, the commentaries that are very well known are: (a) Skandaswamin’s Nirukta-bhashya–tika (14th century), supplemented by Maheshwara’s Vivarana (15thcentury); and, (b) Durga-simha’s Rjvarta (14th century). Durga’s comments are more frequently cited by the later scholars.]
[Hartmut Scharfe in his Grammatical Literature (Otto Harrassowitz, 1977) mentions: The text of Yaska’s Nirukta has come down to us in shorter and longer versions. The word-for-word commentary of Durgasimha (Ca. 13th Century) represents a third or the shortest version.
A study of the versions shows that the text grew in size through many small insertions; and, a new Chapter of Addenda (Parisista – later split into two Chapters 13th and 14th). Even the text commented upon by Durgasimha contains insertions; and , he frequently mentions variant readings.]
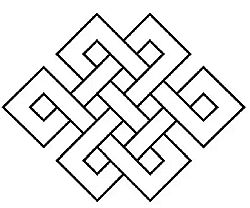
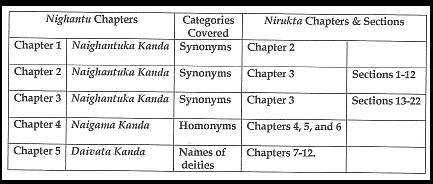
Yaska’s Nirukta comprises twelve Chapters (Parishishta) divided into two broad sections: Purva-shatka (the first six Chapters); and, Uttara-shtka (the latter six Chapters).
These again are grouped into three Kandas (Cantos): Naighantuka Kanda; Naigama Kanda; and, Daivata Kanda.
A. Under the Purva-shatka, which has six Chapters:-
(1) The Naighantuka Kanda, comprises three Chapters (1 t0 3) – Kanda-trayatmaka; and, it comments on the Fourth Chapter of the Nighantu (Naigama Kanda), treating of the words used in the Rig-Veda – commencing with the Gau and ending with Apara.
In this section, Yäska discusses the aims and methods of the Nirukta, as a branch of learning; and, refers to different teachers and contemporary disputes concerning the language and the meaning/s.
Chapter 1 (and part of chapter 2) of Yaska’s Nirukta deals with some important theoretical aspects which gives an insight into Yaska’s overall philosophical and linguistic approach; such as :
: – importance of knowing the meaning of the Vedic mantras;
:- Parts of speech (Padas) classified into four groups (Jatis) (Bheda-chatushtaya)-
(1)Nama (noun);
(2) Akhyata (verb);
(3) Upasarga (preposition); and,
(4) Nipata (particles)
– (Catvari padajatani Nama-Akhyate cha Upsarga Nipata-shcha)
: – Verb-root principle – asserting that the nouns are derived from verbs (dhatuja / akhyataja).
: – Language variation, its causes, forms, and effects
: – Principles of Nirvachana (etymology)
(2) The second Kanda, Naigama Kanda : while the first three Chapters dealt with synonyms (Ekartham-aneka-sabdam); the three Chapters (4 to 6), here, explain the homonyms (Aneka-arthani-ekasabdani); and the Vedic words whose derivation is obscure (Anavagata-samskaran -nigaman). This is called Aikapadikam. This Kanda covers the selected words of the Rig-veda beginning with Jahā and ending with Ulbam ṛbīsam.
(B) Under the Uttara-shatka or the Second Section of Nirukta:-
The Daivata Kanda, in its six Chapters, comments on the Fifth Chapter of Nighantu (Daivata Kanda). It is a systematic exposition of the nature; the symbolism; the forms’ interpretation etc., of the prominent Deities (Devata) of the three regions, of the Earth (Prithvi-sthana), of the Sky (Dyu-sthana); and, of the intermediate space (Madhyama-sthana). It commences with Agni and ends with Deva-patnyah (consorts of gods).
Of those three regions; the Prithvi-sthana covers the deities from Agni to Urjahuti; the Madhyama-sthana covers from Vayu to Bhaga; and, the Dyu-sthana, from Surya to Deva-patnyah.
[Yaska_charya defines a Deva as one who gives gifts (devo daanad), who is effulgent (devo dipanaat), who illumines (devo dyotanad), and who resides in heaven or the celestial world (dyusthane bhavati iti).
devo.dānād.vā.pīpanād.vā.dyotanād.vā.dyu.sthāno.bhavati.iti – Nir.7,15
After discussing the three different views (namely, they have form, they do not have form, and a combination of these two views), the Nirukta concludes that, in reality, there is only one Devata who can be addressed in various ways depending upon the temperament of the aspirant. Yaska_charya confirms by saying Eka atma Bahudha Stuyate (Nir.7,4) meaning there is only One God and many praise by different names.
ekam.sad.viprā.bahudhā.vadanty.agnim.yamam.mātariśvānam.āhuh/”(RV.1,164,46) imam.eva.agnim.mahāntam.ātmānam.ekam.ātmānam.bahudhā.medhāvino.vadanti/ Nir.7.18 /
He further says ; the many forms of gods are manifestation of the atman, One Reality – Ekasya atmanah anye devah pratyangani bhavanti . He emphasizes that the Sat Vastu includes in itself different deities.
māhābhāgyād.devatāyā.eka.ātmā.bahudhā.stūyate,.ekasya.ātmano.anye.devāḥ.pratyaṅgāni.bhavanti- Nir.7.4
Sri Sayanacharya in his Rig_bashya_bhumika says praise of any god leads to the same tat (entity) – Tasmat sarvairapi parameshvara eve huyate .]
[ Devaraja (15th-16thcentury) , a commentator, in the introduction to his work says : Yaska, in his Nirukta, explained, individually , and in their entirety, only the words of which a list is given in the Fourth and Fifth Section of the Nighantu (Naigama and the Daivata Kandas)]
Yaska deals with the etymology proper (Nirukta), with commentary on the related portions of the Nighantu; starting from Chapter 2, Section 2 of Naighantuka Kanda.
Yaska’s commentary (bhasya) commences with a discussion on synonyms (Ekartham-aneka-shabdam). But, later, he devotes more space to elucidating the Nighantu words of obscure nature (Anavagata-samskaran -nigaman), which suggest more than one meaning.
The most interesting portion of the Nirukta is the discussion which covers the whole of the First book and a part of the Second, as well as the Seventh book of the Nighantu, which was as an admirable introduction to the study of the Veda
Yaska’s study included a system of rules for forming words starting from roots and affixes. According to Yaska, every word is derived from a root (Dhatu); and, by analyzing the root, its tendency and the suffix, it is possible to establish the relation between word and meaning.
For Yaska, every term is embedded with meaning (Artha); and, Nirvachana provides the device for doing so. In other words; the meaning is secured by the term itself by Nirvachana analysis, which indeed is the objective way of determining what meaning is ascribed to each word.

As Johannes Bronkhorst writes in Etymology and magic: Yāska’s Nirukta, Plato’s Cratylus, and the riddle of semantic etymologies
A number of rules are formulated in the Second chapter of the Nirukta that should help the student to find etymologies on his own. The most important among these rules is, no doubt, the one that etymologizing should, first of all, be guided by the meaning of the word concerned; phonetic considerations play a less important role:
One should examine a word, being intent upon its meaning, with the help of some similarity in function with other words. When not even such a similarity is present one should explain on the basis of similarity (lakshana) in a syllable or in a single sound.” (Nirukta 2.1).
Tad yeṣu padeṣu svara saṃskārau samarthau prādeśikena vikāreṇa guṇena anvitau syātām tathā tāni nirbrūyād / atha ananvite arthe aprādeśike vikāre artha nityaḥ parīkṣeta kenacid vṛtti sāmānyena / Nir.2,1/
In the case of unknown words, therefore, one looks at the context in which they occur (usually a Vedic hymn), so as to get a first impression as to their meaning. Subsequently one looks for other words (they have to be verbal forms, according to the Nirukta) which are more or less similar to the word under study
Semantic considerations, however, come first. Therefore, a verbal form which is less similar but closer to the expected meaning is to be preferred to a more similar verbal form which does not support the desired meaning. And words which are known to have several meanings have also several etymologies
An example is the word gau “The word go is a synonym for ‘earth’; because, it goes (gata) far; and, because living beings go (gacchanti) on it. Or else, it could be a name of something which moves (gåti). The syllable ‘au’, in the word gau , is a nominal suffix. Moreover, the word gau is the name of an animal (the cow) for this same reason.
Also a bowstring is called gauh; because it sets arrows in motion (gamayati) – Gavyā cet tādhitam, atha cet na gavyā gamayati isūn iti (Nirukta 2.5).

As a part of his exposition, Yaska makes a clear distinction between the Vedic and the spoken language. But, he also observes that sometimes a word used in one is derived from a root belonging to the other. He makes a similar observation with regard to the dialects of regional language (Prakrita)
Atha-apy.bhāṣikebhyo dhātubhyo naigamāḥ kṛto bhāṣyante damūnāḥ kṣetrasādhā iti –Nir.2.2…Atha-api prakṛtaya eva ekeṣu bhāṣyante vikṛtaya ekeṣu –Nir.2.2

The Nirukta, as a discipline , which attempts to determine the essential significance of a Vedic passage (mantrartha), recognizes five kinds of changes that a word in common usage [with Noun (Nama), Verb (Akhyata), Preposition (Upasarga) and Particle (Nipata) ] could undergo to become a Vedic word ; and, to be included in the Nighantu: (1) A letter may be freshly added on to the word (Varna-agama); (2) A letter may be altered (Varna-viparitya); the form of the letter may be distorted (Varna-vikara); (4) A letter may be omitted (Akshara-lopa); and, (5) the root of may get over stressed (Yoga).

Catvari padajatani
In his Nirukta, Yaska tried to explain (Nirvacanam) such Vedic words from the perspective of various linguistic aspects like Noun, Verb, preposition, particle, general definition, special definition, synonyms, homonyms (words that share the same pronunciation but convey different meanings), common and obscure grammatical forms, words and their meanings, and the etymology of these words.
Yaska terms such analytical method as samaskara (treatment) or sastrakrto-yogah (grammatical combination)
In that context, Yaska mentions about the classification of the four groups of parts of speech (Catvari padajatani) such as: Noun (Naman), Verb (Akhyata), Preposition (Upasarga), and Particle (Nipata). Of these, the first two are established by definition; and, the remaining two by enumeration.
Catvāri pada jātāni nāma ākhyāte ca upasarga nipātāś ca tāni imāni bhavanti ...Nir .l.l iti imāni catvāri pada jātāni anukrāntāni nāma ākhyāte ca upasarga nipātāś ca tatra nāmāny ākhyātajāni iti śākaṭāyano nairukta samayaś ca – Nir. 1, 12/
It appears that Audumbarayana, another ancient authority, had not agreed with such four-fold classification of parts of speech
(indriyanityam vacanam Audumbarayanah tatra chatustam Na papayate –Nir.1.1-2).
Yaska opposes the stand taken by Audumbarayana; but then, he goes on to talk about a totally different concept, Bhava – the being and becoming (Bhu) of verbs from their roots. Yaska, in that context, mentions six modes or forms of transformations (Sad bhava vikarah) of Bhava-s from the indistinct (A-vyakta) to explicit (Vyakta) and then to disappearance (vinasa).
These phases are: coming into existence (jayate); existence (Asti); transformation (viparinamate); growth (vardate); decay or wane (apaksiyate); and, ceasing to exist (vinasyati).
These are the six phases of changes (parinama) that do occur in all forms of life or of any entity.

Between the Noun and the Verb, Yaska treats the Verb as the nucleus of a sentence.
Here, though the Noun is named first, it is the Verb that is evidently more important. The Verb expresses action (Kim karoti?), the becoming (Bhava); while Noun, fundamentally, denotes the existing thing – (Sattva – ‘being’).
Here, Sattva is the static aspect of the meaning (as it exists); and, Bhava, the dynamic aspect, is action (Kriya) as it takes place in temporal sequence – (bhavah karma kriya dhatvartha ity anarthantaram).
In other words; a Verb (Akhyata – Bhava pradhana) – is mainly concerned with Bhava (action). Whereas, the Nouns (Naman) have Sattva (substance or existence of an object – Asti- Satva pradhana) as the chief element in their meaning (Bhava-pradhanam akhyatam; sattva-pradhanani namani – Nir. l.l).
According to Yaska, Verb (Akhyata) is the vital unit of language through which we express our intentions and actions; and, a sentence without a verb serves no purpose (tad.yatra.ubhe.bhāva.pradhāne.bhavataḥ – Nir. l. l
bhāvapradhānam ākhyātam/ sattvapradhānāni nāmāni/ tad yatrobhe bhāvapradhāne bhavataḥ pūrvāparībhūtaṃ bhāvam ākhyātenācaṣṭe/ vrajati pacatīti/ upakrama-prabhṛtyapavarga-paryantaṃ mūrtaṃ sattvabhūtaṃ sattvanāmabhiḥ/ vrajyā paktir iti/ ada iti sattvānām upadeśaḥ/ gaur aśvaḥ puruṣo hastīti/ bhavatīti bhāvasya/ āste śete vrajati tiṣṭhatīti – Nir. l.l

Of the four parts of speech (Catvari padajatani) , Yaska gives greater importance to Nouns and Verbs (Naman, Akyata) – which are employed independently – than to the Prefix or Prepositions (Upasarga – Nanavidha vishesha artha pradhana) and the Particles (Nipata – Upamarthe pada puranartha – for the purpose of drawing comparisons), which cannot present a clear meaning when detached from Nouns or Verbs – na nirbaddha upasarga arthannirahuriti Sakatayanah –Nir.I.3.
According to Yaska; Sakatayana held the view that the prepositions are indicative (dyotaka) rather than denotative (vacaka) — (nama-akahyatayostu karmopa-samyoga-dyotaka bhavanti~ Nir.I.3)
With regard to pre-verbs, Yaska refers to the views of Sakatayana and Gärgya: According to the former, the prepositions do not have a meaning of their own; and, when detached from a Noun or a Verb, they do not distinctly express a meaning. But, they do help in highlighting a secondary relation with the object of the Noun or Verb.
But, according to Gärgya, prepositions do have various meanings (even when they are detached from a Noun or a Verb). Their meaning implies a modification in the meaning of Noun and Verb. For instance; Upasarga which is described as Nanavidha vishesha artha pradhana – can provide a special meaning to a word as in A-hara, Vi-hara and Sam-hara.
And, even in its isolated condition, a prefix is capable of modifying the sense of a Verb or a Noun. For instance; the preposition ’A ’ can express the sense of limit , say as in, Apara ( limitless) as opposed to Para (limited). The prepositions Ati and Su indicate excellence, while Nir and Dur are the reverse of the two; Ni and Ava indicate downward-ness, while Ud is the reverse of the two ; and, similarly , Sam indicates junction or togetherness , while Vi and Apa are the reverse of Sam.
Yaska seems to have gone along with Gargya’s view . he enumerates twenty Upasargas.
nāma.ākhyātayos.tu.karma.upasamyoga.dyotakā.bhavanty/ucca-avacāḥ-Pada-arthā. Bhavanti iti.Gārgyas/tad.ya.eṣu.pada.arthaḥ.prāhur.im.tam. Nāma.Ākhyātayor-artha-vikaraṇamā.ity. arvāg.arthe.pra.parā.ity.etasya.prātilomyam – Nir.1.3 .
When that logic is extended, it leads to say: the phonemes and syllables are not independent entities conveying their own meaning. Nevertheless, they are the essential parts of the word. But, the meaning of the word does not solely arise out of them. The Meaning is the function of the word as a whole.
[Patanjali, in his Mahabhashya puts forward a similar argument.
For the purpose of illustration; he cites the three words Kupa (well); Supa (soup); and, Yupa (sacrificial post).
Here, Patanjali points out; the first letter of each of those three words differs; but, the other letters that follow are identical. These are, in fact, three separate words that are distinguished by the substitution of one phoneme, for another phoneme
However, the object signified by each one is distinct from the objects signified by the other two words. Each of the three words signifies a different object.
Patanjali says; each of the phonemes – K; S; and Y- does not by itself carry a meaning. Similarly, the set of other letters in the three words (- upa) also, by itself, does not make any sense. It is only when they combine, a word carrying a meaning, is put forth.
Patanjali compares this fact to a chariot made of several parts; where, each of its parts, by itself, is incapable of moving. It is only when all the parts combine systematically and form a single entity that the chariot can move.
Thus, Patanjali argues that phonemes have a differentiating significance within the units which bear the meaning. Such a unit, he considers it as saṅghāta, a single entity which is ‘indivisible and one’. A phoneme, thus, plays a significant role in distinguishing one word from the other, each pointing to a different object.]
In Yaska’s Nirukta, the Upasargas were used with the nouns and also with Verbs – nāma.ākhyātayos.tu.karma.upasamyoga.dyotakā.bhavanty (Nir.1.3).
[Yaska enumerates twenty prepositions, along with their meanings: ati-;adhi-;anu-;apa-;api-;abhi-;ava-;aa-;ut-;upa-;dus-;nis-;nir-;paraa-;pari-;pra-;prati-;v; sam-;and su-. And, to that list, Sakatayana adds three more Upasargas: accha-; srad-; and antar-. Later marut-; and dur- were added; thus making it to 25.]

One of the main features of Nirukta is that Yaska agrees with Sakatayana that all nouns are derived from a verbal stem (mula); and, all nouns are regarded as related to an activity expressed in language by a verbal form – tatra nāmāny ākhyātajāni iti śākaṭāyano nairukta samayaś ca / na sarvāṇi iti Gārgyo vaiyākaraṇā-nāṃś ca eke – Nir. 1, 12/
Yaska says: any Noun can be traced back to a root (Dhatu), similar in form and meaning – samāna karmāṇo dhātavo dhātur dadhāteḥ. And with that, all words come under the purview of the Nirukta.
[As compared to that, Panini left aside the irregular formations. Further, Nirukta also comments on those Vedic passages, words and their forms , which were not analyzed in the texts of Grammar. And, therefore, Saroja Bhate remarks, the function of Nirukta starts when that of the Grammar ends. And, therefore, Yaska aptly describes his work as ‘the completion of Grammar’- vyākaraṇasya kārtsnyam- [tad idam vidyasthanam vyakaranasya kartsnyam svartha-sadhakam ca . (Nir. 1,15) ]
Yaska considers the verbal roots (Dhātu) to be the bases (prakṛti), and their noun-forms to be the modifications of them (vikṛti); and, he calls the latter as ‘born’ from the former.
As the nouns, often, have verbal roots (Dhatu), they attempt to explain ‘Why something is called what it is called ‘, by linking it to some activity; thereby establishing its relation to a verb or verbal-root. In fact, Yaska treats every noun as an information-invoking singular term.
For instance; the Nirukta states that the noun Cittam (mind) is derived from (the root) its activity cit (to know) – cittaṃ cetateḥ (Nirukta 1.6)
The logic behind Yaska’s assertion appears to be: man keeps creating more new words to conceptualize and to describe verities of actions; which is to say, both the meaning and the etymology of words are always context-sensitive.
Thus, His main view is that the name of an object is to be determined by its actions, as also by the contextual factors (samsarga etc.)
*
The proposition that the Nouns are derived from Verbs (dhatuja/akhyataja) was opposed by many grammarians, including Gargya. They argued that if all nouns were derived from verbs, every person who performs a particular action should have the same name. [Kartri (a doer) from Kri (to do); Pachaka (cook) from Pach (to cook), and so on]
Yaska rebutted such criticisms by pointing out: Not everyone gets the same name by performing the same action. For instance; a carpenter performs many other actions (takṣatiḥ karoti karmā), besides cutting the wood. The term ‘Carpenter’, here, signifies a person, who possesses a distinctive skill; and, perhaps follows a particular profession for his living. It does not, however, refer to any one particular person. It could refer to a whole class of such persons, in general.
But, anyone or everyone who cuts wood cannot be called a carpenter (takṣā).
Thus, though one is involved in many different activities, one gets his name from a particular action in which he is engaged. Therefore, objects are named depending upon the specific actions they perform.
yaḥ kaś ca tat karma kuryāt sarvam tat attvam tathā ācakṣīran / yaḥ kaś ca adhvānam aśnuvīta aśvaḥ sa vacanīyaḥ syāt / atha api cet sarvāṇy ākhyātajāni nāmāni syuḥ / Nir.1,12

It is said; the Grammarians classify the meanings of a word under three categories: Yaugika; Yogarudha; and, Rudha.
When a word expresses its etymological sense, it is called Yaugika (derivative);
When its etymological meaning and its conventional meaning are the same, it is called Yogarudha (derivative and conventional) ; and,
When the conventional meaning, the one that is used in day-to-day affairs, is either not directly connected with its etymological derivation or it is different, then it is called Rudha (conventional).
But, as rule, the conventional meaning is regarded as stronger as and more acceptable than the etymological meaning (yogad rudhir baliyasi sighravrttitvat).
For instance; the etymological meaning of the term Asva is that which pervades or occupies; but, Asva in common usage denotes a horse. Similarly, Pankaja etymologically means that which is born in slush; but, it is commonly used to indicate a lotus flower.
The other is the Ashva-karna a type of leaf; but literally, the ears of a horse. In all such cases, it is the meaning in common usage that is generally accepted; and, the literal meaning is treated as faded metaphor.
Following the same principle, and citing the same instances, Matanga, in his Brhaddeshi, explains: whatever might be its other meanings, the word Raga (derived from the root ranj = to please), effectively suggests, here, as that which generates delight: Ranjana-jjayate ragau.
Ithevam raga-shabdasya utpatthir abhidiyate I Ranjana-jjayate ragau utpatthih samudahrutah II283II Ashva-karnadi vidha rude yaugikau vaapi vachakah I Yogarudosthva raage jneyam pankaja-shabdavat II 284II
[Panini also said that the meanings of the words were bound to change with the passage of time, as also in varying contexts. He recognized the fact the people who spoke the language and used it in their day-to-day lives were better judges in deriving, meaning from the words.
Strangely, that came true in the case of Panini himself. For instance; in the Astadhyayi (6.1.147), the word ‘Ascharya’ is explained as that which is not-permanent (Anitya) or rare: āścaryam-anitye. And, Katyayana, a couple of centuries later, corrected that meaning to imply ‘Adbhuta’ – something that is wondrous, miraculous or unprecedented. The meaning of the term ‘Ascharya’, as interpreted by Katyayana has, of course, prevailed; and , is in common use now.
The term Aranyaka is interpreted by Panini to mean ’a forest dweller, a man who lives in the forest’- araṇyān-manuṣye (P S 4.2.129). And, Katyayana expanded its meaning to include a class of Vedic texts. But, somehow, it is not applied for referring to forest elephants, jackals and other wild animals that also live in the forests.
Bhartrhari, in his Vakyapadiya, therefore, emphasizes the importance of contextual factors in the determination of the meaning of expressions. Etymology is without doubt important in its own context; but, in the day-to-day conversations (rudi) the conventional meaning (Vyvaharica-artha) takes precedence over the etymologically derived sense
It is often said; a Grammarian may have control over the Lakshana (the rules); but, not always over the Lakshya, the way the language is used in the outside world. The quality of such language is almost excellent, when it is immediately close to the grammatical rules. But, many a times, the Lakshana becomes subservient to Lakshya. ].
[The American Dialect Society, which studies the evolution of language, has voted
the neutral pronoun “they” as the word of the present decade. “They” is used in English by a growing number of non-binary individuals, people who do not identify as either male or female. They prefer the plural neutral pronoun to bypass the traditionally male “he” or female “she”. Thus, it is said “they” has become an indication of “how the personal expression of gender identity employed by an increasing part of our shared discourse.”]

After explaining the evolution of speech; and, the fourfold stages of speech, Yaska takes up the question: — ‘whether the words are eternal or ephemeral, merely created for the time being’.
Besides the issue of the eternity of words, Yaska also talks about the infallibility of Vedic words, the impermanence of human knowledge etc., – karmasampattir mantro Vede– Nir.I.2.; Purusa vidya nityatvat – Nir.I.2
Yaska asserts that the word, the meaning and their mutual relations are eternal (nityam vacanam).
Yaska brushes aside the prima facie view (Purva-paksha) or the objections raised by Audumbarayana and such others; and, argues: If we admit the impermanence of words, then the mutual relation and the grammatical relation of words are not possible. Therefore, the functions of words are possible only if we admit they are everlasting, in their nature.
Following the Mimamsakas, Yaska also supported the doctrine of the eternal nature of the words – ‘vyaptimattvat tu sabdasya’ (Nir.I.2)
In this way, Yaska believed in the idea of the eternity of words; and, then he engaged in the Sphota theory. This Doctrine (Sphota-vada) puts forward the view: When a word is uttered, it reaches the mind of the listener through her/his ears; and, on its acceptance, the mind absorbs and understands the sense of verbal-sounds it received. Thus, the uttered words, which travel through the air, perish. Yet, the meaning conveyed by them resides permanently in the mind of the listener.
Yaska was, perhaps, one among the earliest authorities to make a reference to Sphota-vada. Bharthari (11th century) in his celebrated work Vakyapadiya acknowledges Yaska’s reference to the Sphota concept. Bhartrhari explains the Sphota as: a spontaneous process where a latent idea or thought arising out of the consciousness or the mind of the speaker is manifested by the sounds (Dhvani) of the spoken words employed in the sentence; and, it is directly grasped, through intuition (Prathibha), by the mind (Buddhi) of the listener.
In this context, Yaska mentions that the words, obviously, carry a meaning; but, in the course of time, a word might acquire a meaning that is different or even quite opposite to the one it had earlier. Such a change of meaning possibly comes about due to various reasons. That might be because, in the later times, it may to have to indicate a different type of action, object or an usage. And, that often happens; because the name of an object is to be determined by its actions. Therefore, the contextual factors (Samsarga) , in their current time, become important in arriving at the new meaning of a term.
Answering the question – how an object could be called by a certain name, when it is performing a different action than that is indicated by its name, Durga, commenting on the Nirukta, says: šabda-niyamaḥ svabhāvata eva loke – “in spoken language, in the world , the usage of the word (Sabda-vrtti) follows its own nature”.
According to Durga , this svabhāva is an inherent characteristic of the word, as a meaningful entity. It has its own existence; and , can ,therefore, be applied to any object at will by a speaker, thus creating a new contextual meaning; because, the word in its semantic aspect, continues to carry its own significance .
Durga remarks: the use of words, their role and the intended effect are context sensitive. The same word could be employed in any number of ways; each performing its role its own context. Therefore even on the purely communication level, the word acts as a meaningful entity, influencing and creating the society of man, which is nothing but a product of this communication.
The Scholarly Paper Yaska’s discussion of the meaning of a word in relation to objective reality, explains:
A word persists in its own reality beyond the reality of time and space. Since we live, act, see, understand the world using our linguistic reality, the name once given to the object, whether it was relevant or seemed to be relevant for a particular speaker, could remain for a longer time, even if it had very little to do with the current action of the object. The reason why this or that name was given to the object was not in order to satisfy an objective reality. But, rather, it was a subjective one; for, it was named by a speaker imposing his wish, opinion, knowledge or will on the object. Once the name has been used, it would persist in memory until a new name effaces or changes it; or even, it might perhaps, last longer.

Finally, as Eivind Kahrs in his Indian Semantic Analysis: The Nirvacana Tradition sums up his review of Yaska’s work, says:
What is really important about the Nirukta is that it is the single text we possess which applies a certain method designated to give semantic analysis of nouns, in the widest sense of the term. Moreover, Nirukta contains lengthy discussions of linguistic and philosophic import. As compared to Panini’s formal grammatical attitude, keeping out the philosophical notions; Yaska’s interest in philosophy is remarkable.
Though the main task of the Nirukta of Yaska is to explain most of the rare and obscure Vedic words by pointing out various possible etymologies , there are also discussions of general nature, on the concept of eternity and infallibility of Vedic words, (karma-sampattir mantro Vede – Nir.I.2); the impermanence of human knowledge (purusa-vidya-anityatvat – Nir.I.2) and so on. Thus, Yaska’s commentary is not restricted to derivation of Vedic words, but covers a much wider field.

Before we proceed to talk about Panini, let us briefly, in a capsule form, jot down the significant differences between the Nirukta of Yaska and the Astadhyayi of Panini.
(1) Nirukta is a glossary commenting and explaining the meaning of certain chosen mantras of the Rigveda, based mainly on the Nighantu and the Brahmana texts. Its focus is on the Vedic language.
Astadhyayi is an independent and an original treatise, seeking to construct a systematic analysis of all speech forms.
(2) The main task of the Nirukta is to provide the exact meaning of antiquated terms of the Rigveda that were no longer in use. It, basically, is rooted in the past.
The Astadhyayi is, principally, concerned with the language that is alive and is evolving. It deals with the then present status of the language; refining its form and usage. It strives to ensure the correct treatment of the words by purifying (Samskrita) the language (bhasha) – literary and spoken (vaidika and laukika) – that was in use during its days.
It also serves as authoritative guidelines, for the future generations, for understanding the language, speaking it correctly and using it, as it should be.
The content and the scope of Astadhyayi is much wider, as compared to that of the Nirukta.
(3) Yaska’s Nirukta is written in easy flowing prose. It hardly needs a commentary, to explain or to interpret its content.
Panini’s Ashtadhyayi is composed in Sutra form-terse and tightly knit; rather highly abbreviated. The text does need a companion volume to explain it. Therefore, generations of Grammarians and scholars were engaged (and continue to be engaged) in commenting upon and in elucidating Panini’s text.
**
Johannes Bronkhorst in his scholarly paper, Nirukta and Aṣṭādhyāyī: their shared presuppositions, after making a comparative study of the two texts concludes :
The Nirukta and the Astådhyåyi can be looked upon as rational elaborations of the same set (or closely similar sets) of presuppositions. Both assume that the meaning of words and larger utterances is the sum of the meanings of their separate parts.
The author of the Astådhyåyi set out to show in detail how these small units of meaning, these semantic elements, find expression in the phenomenal language.
The author of the Nirukta, on the other hand, used his supposed knowledge in a different way. He developed a method with the help of which every word, however obscure it might seem, could be forced to yield its meaning to the investigator. He also tried to give strict rules that should be observed while using his method. The nature of his endeavor, however, brought about that these rules could not be as strict as the ones that govern grammatical derivations.

References and Sources
- The Nighantu and the Nirukta by Sri Lakshman Sarup
- Text of the Nirukta – Based on the edition by Sri Lakshman Sarup
- Ashtadhyayi or Sutrapatha of Panini
- A critical study of some aspects of Nirukta by Tarapada Chakrabarti
- Etymology and magic: Yaska’s Nirukta, Plato’s Cratylus, and the riddle of semantic etymologies by Johannes Bronkhorst
- Grammatical Literature by Hartmut Scharfe
- Indian Semantic Analysis: The Nirvacana Tradition by Eivind Kahrs
- Yaska’s discussion of the meaning of a word in relation to objective reality
- Pānini and Yāska : Principles of derivation by Saroja Bhate
- Yaska’s Nirukta and his reflections on language
- The Nirukta and the Aitareya Brahmana by Prof. Viman Ch. Bhattacharya
- The History of Indian Literature (1892) by Albrecht Weber
- Introduction to the Nirukta and the literature related to it by Rudolph Roth
- Panini and his place in Sanskrit by Theodor Goldstücker
- Yaska’s Nirukta by Prof. S. K. Ramachandra Rao
- Linguistic observations of Yaska
- https://www.academia.edu/3287928/Nirukta_and_A%E1%B9%A3%E1%B9%AD%C4%81dhy%C4%81y%C4%AB_their_shared_presuppositions?email_work_card=view-paper
- All images are from Internet