Sri Shyama Shastry – Music-Continued

The Kriti is a composite Art form. A good Kriti is the sublime blend of the Mathu (Sahitya) and Dhathu, the Music and its rhythm. All the constituent elements (Angas) – the sentiment, the diction, the music and the rhythm– that combine to form a Kriti, have to be in harmony, supporting each other; each helping the others to shine forth and to manifest in their best form. The Kriti is indeed a living, fluid, organic entity.
In the Karnataka Samgita, Mathu or Sahitya and the prosody (Kavya-lakshana) assume great importance. Raga, essentially, is a representation or an outpouring of the emotional content (Raga-bhava) of the Kriti, evoking a distinct feeling of happiness, sweetness (Madhurya) or poignancy (Karuna-rasa). But, Raga, by its very nature; is rather amorphous; and, truly having no physical or material existence. It does need a medium to articulate in a tangible form that draws the listener into the music; and to communicate with her/ him. It is only then there will be fulfillment (Dhanyata-bhava); and, music becomes a shared experience between the composer, performer and the listener.
And, even otherwise, the lyrics of a Kriti has its own importance. A composition is known and recognized by its Sahitya; particularly by it’s opening lines (Pallavi), than by the mere name of the Raga, which attires its lyrical appeal. There might be numerous Kritis in a particular Raga; but, it is its Sahitya that lends an identity to a given composition.
A well composed , expressive , lyrical beauty that blends amicably with melody and rhythm is a distinctly bright feature of the Karnataka Samgita. Perhaps no other system of music, anywhere in the world, can boast of such a wealth of exquisitely structured compositions set to music.
If an erudite composer also happens to be a gifted poet, endowed with innate poetic genius (Kavya-Prathibha), which is nurtured and developed through training Utpatti (detailed study of Grammar, the literary works and scriptures); and Abhyasa, Abhiyoga, Prayatna (constant practice) of composing poetry set to Music, then his Kriti will blossom into most delectable poetic presentation adorned with enjoyable music and pulsating rhythm.
It creates an idyllic ambiance that is shared by the creator, the performer and the Rasika (enjoyer). It, somehow, touches the very core of our being. And, as Abhinavagupta says, it is a Chamatkara, which bestows on all an Alaukika Ananda, an out-of-the-world wondrous aesthetic joy. Thus, at the end, very little would separate the composer, the singer and the Sahrudaya, the well informed connoisseur.
In the traditional kritis, composing a Sahitya that conforms to the laws of the prosody (Kavya Agama) is very vital. All the renowned composers of the Karnataka Samgita were well learned in Vyakarana, Chhandas and other Prayogas of Padya Sahithya. Their Kritis show the remarkable mastery they had gained over the Alamkaras – literary embellishments—such as: Prasa, Yati, Yamaka, Gamaka, Svarakshara patterns and others.

Prasa
Prasa is a type of Sabda-alamkara, a literary ornamentation. The term Prasa refers to the sound or the phonetic sequence. In a composition; similar sounds (Prasa) could be employed either at the commencement of each Paada (line) of the composition (Adi or Adyakshara-prasa); or as ‘Anu-prasa’ , where similar letters or sounds recur repeatedly in the same Paada; or in the second syllables of each Paada (Dvitiyakshara-prasa); or in the concluding line where the rhyming occurs towards the ending (Antyakshara-prasa).
And, Adi or Adyakshara-prasa, mainly, involves rhyming, where each Paada (line) starts with the same Akshara; or, where the first letter is repeated between the Avartas.
Anu prasa is where similar letters recur repeatedly in the same Paada.
Dvitiya-kshara-prasa is the repetition of the second letter (Jiva-akshara) of the first Avarta in the same position in the subsequent Avartas, as well. This is concerned only with consonants, not vowels. Such a Prasa can be for a single letter and also for a group of letters.
Antya-prasa is the repetition of a letter or group of letters at the end of the Avartas. It differs from Prasa; because, while the Prasa is confined to consonants, here the vowels are also included. For instance, a word like Netram can have Antyaprasa only with words like Gatram, Sutram, etc., and not with words like Satrum, Atrim etc.
The Muhana is the repetition of the first letter between the Avartas. The Antya-prasa is the repetition of a letter or group of letters at the end of the Avarta.
Muhana is a type of Sabdalankara, in which the same letter as in the beginning of an Avarta or any of its substitutes should occur in the beginning of the second Avarta. For example,‘ Dinakara Kula dipa / Dhrita divya sara chapa!’
The term Antar+ukti, literally means the ‘in-between utterance’. The method of Antarukti is by way of inserting one or more syllables between two words. It is done mostly for the sake of maintaining the flow of the Taala.
**
In the Kritis of Sri Shyama Shastry, many of which are technically classified as Telugu works, the essential and the prime body of the lyrics is in chaste, refined classical Sanskrit-based terms.
His Telugu words, though often are informal and colloquial expressions, are infused with emotion trying to express the natural feelings of tenderness, love and affection of a child reaching out to its Mother. Many of these songs are a sort of conversations, pleading with the Mother, questioning her why she is not paying attention to him, not responding to his desperate appeals and so on.
And, in such Kritis, though he has mostly employed the spoken form of Telugu language, either as verbs (Akhyata) – say like brovu, vinu, matladu etc. or for addressing (Sambhodana) the Mother Deity as Talli, Mayamma etc., the string of sweet-sounding names and eloquent, picturesque adjectives he uses for describing the beauty, splendour and the countless virtues of the Supreme Mother Goddess are all in delightful Sanskrit phrases.
*
Further, the nature of the Telugu- Sahitya of his Kritis markedly differs from the Sahitya of the Svarajatis.
The Telugu-Sahitya of his Svarajatis, in contrast, is more poetic; orderly and, is often interspersed with philosophical expressions.
*
Sri Shyama Shastry has adopted the time-honored (Sampradaya-baddha) poetic traditions (Kavya-agama) followed in the ancient Prabandhas as also in the Kirtanas and Kritis that came into being during the seventeenth and the eighteenth . Such essential poetic virtues (Kavya-guna) are found in the Kritis of the other Masters also.
Many of the Kritis of Sri Shyama Shastry are adorned with the metaphors of Kavya-Alamkara and Sabda-Alamkaras, such as Anuprasa and Antya-prasa. And, Muhana (the first letter repetition between the Avartas) and Prasa (the second letter repetition) are also used. But, more Kritis are found with the Prasa-Yati. Sri Shyama Shastri used the method of splitting up the words i.e. Antarukti for introducing Prasa- Yati
Smt. Sharadambal explains : with regard to the occurrence of the Prasa-aksharas in the compositions of Sri Shyama Shastry, they can be divided into four categories,.
- Dhirgha (long) syllables preceding the Prasa-akshara in the Carana alone.
- Dhirgha (long) syllable proceeds in the all the three Angas.
- Hrasva (short) letter is found throughout the composition.
- 4. Dhirgha (long) syllable is found in Pallavi and Anupallavi; and, the Hrasva (short) syllable is used in the Carana.
This Kriti ‘Devi nee paada sarasamule’ (Khambhoji); and, Mayamma (Ahiri) are cited as instances, where both the long and the short syllable are used in the Kriti.
**
Sri Shyama Shastry used the Prasas like Adi-Prasa; Anu-prasa; Dvitiya-kshara-Prasa and Antya-Prasa.
For instance; the Sambhodana-vibhakthi, as an Adyakshara-prasa is used in Sri Shyama Shastry’s Kriti ‘Emani Migula’ (Todi).
Here, every Paada (line) of the second Carana commences with similar sounds, calling out to the Divine Mother: O Janani Karuni…. Om Anina Janma … O Moha- vratulai … O Rajadhi-rajendra.
*
Examples of alliteration of the first letter
Saroja-dala-netri (Shankarabharanam)
Saroja dala-netri Himagiri-putri nipada-mbujamule
Sada nammina-namma subhamimma Sri Minakshamma
Mariveregati (Anandabhairavi)
Madhura-puri nilaya vani rama sevita pada kamala
Madhu kaitabha bhanjani katyani marala-gamana
*
Sri Shyama Shastry has employed Anu-prasa (repetition of a vowel or consonant or both), in some of his Kritis. For instance; in the Kriti ‘Kanaka-shaila’ (Punnagavarali), the syllable ‘da’ is repeatedly used in the second Carana as follows:
Chanda-munda-kandana-panditesu;danda-kodanda-mandita-pani; pundarika -nayana-archita-paade
In the Kriti Parvati Ninnu (Kalkada) the Anuprasa is seen in many places such as:
Anupallavi: Sangita-lole, Suguna-jale, and Jala- mele
Carana-1:Banda-daitya-Khandana-Khandala-vinuta-Mârthand-Neeraja-kshi Nikhila-sakshi
Carana(2):Indu-vadana-Kunda-radana-Sindura-gamana-makaranda-vâni,Nila megha-veni Girvani.
*
In the First Carana of the Kriti O Jagadamba (Anandabhairavi), the Dvitiya-kshara Prasa for the sound ‘Inna’ occurs in all the four Avartas, till the last line:
Kanna-talli;- Kannada-salupaga ;- Ninnu-ne; – Anni-bhuvana ; – Prasanna-murti; -Vinna-pambu; Vipanna-bhaya
*
And , in the Kriti Meenalochana (Dhanyasi) the Dvitiya-kshara ’Na’ has been maintained in the Anupallavi and in the First Carana as ; Meena; Gana; Kanna; Panna etc.
In the Anupallavi of the Kriti Saroja-dala-netri (Shankarabharanam), the letter ‘ra’ occurs as the second (Dvitiya) letter (Akshara) of its lines.
Paraku seyaka varadayaki nivale daivamu-lokamulo-galada
Purani sukapani Madhukara veni Sadasivuniki rani
*
Sri Shyama Shastry used the device of Antarukti for splitting up the words, for introducing Prasa-yati, in some cases.
In the Kriti O Jagadamba (Anandabhairavi), the Antarukti is used to bring the Prasa Yati.
Pallavi: O Jagadamba nannu (Na…..- Antarukti Vujavamuna) brovumu …..
Anupallavi: Rajamukhi ……. (Suguna –Antarukti Rajarajita) Kamakshi
*
Antya-prasa is found in all the three Angas of Sri Shyama Shastry’s Kriti Shankari Shamkaru (Saveri), where the Pallavi reads: ‘Akhilandeshwari–Vandite Gauri’.
That is followed by Anupallavi: Kalyani–Jagatjanani; and, First Carana: Jagadavanollasini—Kapaladarini sulini
*
Another type of Antya-prasa used by him was to repeat the same word at the end of all the Caranas.
For instance; the word ‘birana’ is repeated at the end of the Pallavi and at the end of the last line of all the three Caranas of the Kriti Brovavamma (Manji).
Similar is the case with the word ‘Na-talli’ in ‘Devi brova samayamide’ (Chintamani) ; and , the word ‘Brochutaku’ in the Kriti ‘Ninnu-vinaga’ (Purvikalyani)

Yati
Yati is a generic term, having different connotations in Kavya, Taala (Mrdanga) and in Music. In regard to the Kritis in Karnataka samgita, Yati is a Dhatu-Mathu-Samyukta Alamkara. This Anga is meant to decorate the texture of the compositions. Yati could also control the arrangement of various tempos. It is, thus, an ornamentation that enhances the beauty of the Sahitya and the flow of the Musical presentation of the Kriti.
If the Yati is taken to mean the arrangement of Sahitya phrases along with its Dhatu, there would be different types of Yatis in music. Here the Sahitya phrases would be ingeniously arranged to form varied patterns, such as: Sama Yati, Gopuchcha Yati, Srotovaha Yati, Damaru Yati, Mridanga Yati and Vishama Yati.
Sri Mutthuswami Dikshitar, in particular was a Master in crafting such various patterns of Yatis. And, some Yati-prayogas are also seen in the Kritis of Sri Thyagaraja. But, Sri Shyama Shastry did not seem to have attempted Yati-prasa to that extent; except perhaps the Sama Yati, which is an even flow of the Sahitya phrases; and, follows a uniform length of lines (Sama). If two letters of Yati and Prasa are of one and the same character and magnitude, it is called as Sama-yati -Prasa.
According to Prof. Sambamurthy, alliterating the initial syllables or their sequence in Avartas could be taken as Yati. The purpose of the Yati is to create a pleasant musical resonance.
In Sri Shyama Shastri Kritis, the Dhatu as well as its rhythm are arranged; for example; in the Kriti Palainchu-Kamakshi (Madhyamavathi), the phrase ‘Paalinchu Kamakshi pavani …..Paapa-shamanee‘, the appearance of the second Pa is called Sama-yati-Prasa.
In the Kriti Mayamma (Ahiri), the Yatis that occur are of the same character and magnitude.


Yamaka
This is a literary beauty, where in the same word, will be repeated but with different meaning and sense. For instance; In the Anupallavi of the Kriti Mayamma (Natakuranji), the word ‘Ananda‘ is applied in many ways so as to give different layers of meaning (True bliss -Happy one – Eternally blissful -Blissful):
Saty(A)nandA – SAnandA – Nity(A)nandA –AnandA

Gamaka
The term Gamaka derived from the root ’gam’ suggests movement (Gamana, Gamya). Gamakas are graces or ornamented flourishes of the Svaras which characterize the gait of a Raga (Raga-sanchara); and, establish the melodic nature of the Dhathu of a musical composition (Raga-svarupa). They are the varied musical effects (Alamkaras) that can transform a plain note into something that is attractive, charming and pleasant on the ears (Gamakau–srotra-sukhadai-lalithair-asthu).
Parsvadeva, in his ‘Sangeetha Samaya Sara’ defines Gamaka in the following terms :- “When a note produces the color of srutis other than those which are its own, it is known as Gamaka.”
Gamakas are executed in varied forms, such as: graceful turn, curve or sliding touch given to a single note or a group of notes, which animates Svaras to bring out the melodic character and expression (bhava) of a Raga. Gamaka-rendering is a highly individualistic and a specialized skill. Gamakas are very vital factors of Karnataka Samgita. I am not sure if any other system of music has a worthy equivalent to Gamaka of Karnataka Samgita.
Gamaka (ornamented note) is thus any graceful turn, curve or cornering touch given to a single note or a group of notes, which adds emphasis to each Raga’s unique character. Gamaka, in short, is the movement of Svaras which bounce, slide, glide, shivers, rapidly oscillates or skips. It provides movement and animates Svaras to bring out the melodic character and expression (bhava) of a Raga. Each Raga has specific rules on the types of Gamakas that might be applied to specific notes, and the types that may not. Every Raga has, therefore, to be necessarily rendered with the appropriate Gamakas. They depend on the manner of quivering, oscillations or shaking that the Svaras can be endowed with.
Sarangadeva (11th Century) in his Sangita-ratnakara , enumerates fifteen (pancha-dasha) varieties of Gamakas –
Tiripa, Sphurita, Kampita, Leena, Andolita, Vali, Tribhinna, Kurula, Ahata, Ullasita, Humpita, Plavita, Mudrita, Namita and Misrita
Although the Gamakas are formally listed as fifteen, Sarangadeva remarks, the Gamakas are indeed countless.
And, while describing the virtues and the desired qualities of a highly accomplished singer (Uttama Gayaka) who belongs to a good tradition (Su-sampradayo) , Sarangadeva says, such a one should have the intelligence to improvise the Gamakas in all their movements (Sarva-sthanao-ttha-Gamake-sarva-kaku-vishesha-vit,-aneka-sthai- sancharah); and, in all the three registers (Sthanas)
*
The Kritis of Sri Shyama Shastry are remarkable for their Gamaka Prayogas. His Kritis, set in leisurely Vilamba laya, excelling in Chowka kala, are ideal for illuminating and elaborately bringing out the varied nuances of a Raga through the application of many improvised Gamaka movements like Kampita, Jaru etc..
As a composer of great merit, Sri Shyama Shastry creatively transformed the traditional concept and application of the Gamakas. In his Prayogas, the Gamaka is not a mere ornamentation of a Svara; but, it is also a soulful means of expressing anguish, devotion, joy and such other emotions. It lends a new color and a new dimension to both the Dhatu (Music) and the Mathu (Sahitya) of his Kritis. Sri Shyama Shastry was indeed a pioneer in delineating the Raga-bhava through Gamaka Prayoga.
Any number of instances could be cited in this regard. But, just to mention a few:
His different compositions in Anandabhairavi bring out diverse shades and aspects of the Raga. It could be either a simple delineation of the Raga as in his Kriti ‘Himaachala-tanaya’; or the Jaru Gamakas (glides) in the Madhyama-kala tempo in Rupaka Taala as in the Kriti ‘Pahi Sri’; or it could also be the Jaru Gamakas in Vilamba-kala set to Misra –Chapu-Taala as in the Kriti ‘Marivere’; and, finally, it could be an elaborate Raga portrayal in the Adi Taala , Madhyama gati, in the Kriti ‘O Jagadamba’.
The two varieties of Kampita -Gamaka are applied to the same phrase ‘Amba ni’ in the Kriti ‘Sari-evvaramma’ (Bhairavi) to express two different emotions. Similar features can be seen in his other Kritis also.
In the Kriti ‘O Jagadamba’ (Anandabhairavi), the opening exclamation ‘Oh’ is repeated thrice, with three different Gamakas. Initially, it is in a lower Svara, as an Etra-jaru (a glide from a lower Svara-sthana to a higher one). The second ‘Oh‘ is expressed through oscillations (Kampita) in higher notes, in a circling movement. And, the third ‘Oh’ is an Erakka-jaru (a slide from a higher Svara-sthana to a lower one).
In the Svarasahitya of the Kriti Kamakshi Bangaru (36-Varali, Misra Chapu), where the word ‘Mayamma’ starts with a Jaru (glide) from the Daivata; and, reaches Tara-shadja in the passage ‘Mayamma Vegame Karuna-judavamma’
*
Many examples of Gamakas can also be found in Sri Shyama Shastry’s Svarajatis. His Todi-Svarajati ‘Raave’ begins with a Mandra-sthayi-Dheergha-Dhaivata, which is sung with Kampita Gamaka (oscillations).
His very famous Bhairavi Svarajati ‘Kamakshi’ has eight Caranas starting in the ascending order, the Arohana, as ‘Sa RI Ga Ma Pa Dha Ni Sa’. In the opening lines of the Pallavi, which are in Mandara Sthayi, in a contemplative mood, the Kampita (oscillation) and Jaru (glides) Gamakas follow in succession.
The Yadhukula-kambodhi Svarajati has many instances of Jaru Gamakas as well as the Pratyahata Gamaka (Sphurita in the descent, a Samabandha Gamaka produced from the higher note in a Janta svara prayoga), which is a characteristic of the Raga.
*
Even in his Varnas, there are many Gamaka-prayogas.
For instance; the Varna in Anandabhairavi, ‘Sami ninne’ not only begins with a characteristic Jaru Gamaka (s/s-d-p-m-g-m); but , it also appears at many other parts of the composition.
[For a detailed discussion on the Gamakas, please do read the Chapter 5 – Concept of Gamaka in the compositions of Syamasastri– of Dr.Manju Gopal’s research paper.]
[** Svarajati, as the name suggests, is a combination of Svaras (notes) and Jati (rhythmical sol-fa passages). Sri Shyama Shastry revised the form of the Svarajatis by eliminating the Jatis; and, letting the Svaras to arrange themselves into Jati-patterns. The Svarajati composition commences with a Pallavi; and, is followed by Carana/s. While rendering the Carana, the Svaras are sung first; and, then its corresponding Sahitya is presented.
The beauty of the Svarajatis composed by Sri Shyama Shastry is in its natural flow of the Taala, Laya and Svaras. ]

Taala and Laya
Taala and Laya, over which Sri Shyama Shastry had gained mastery, and their dexterous combination with the Sahitya are among the outstanding features of his compositions.
He had experimented with altering the sequence of Matras in the Misra Chapu, transforming it into its reverse, the Viloma Chapau.
He had employed various Grahas or Eduppus (starting Points) in his Misra Chapu Kritis.
*
Sri Subbarama Dikshitar (on page 15 of the segment Vaggeyakara Caritam included in his monumental work Sangita Sampradaya Pradarshini), while writing a biographical note about Sri Shyama Shastry says;
Since his compositions are like ‘narikela-paka’ ”(as tough as breaking a coconut), with rich poetry, containing Atita, Anagata Grahas , with beautiful words, some lazy musicians, who could neither comprehend nor had the mettle to sing them in the manner that pleased the audience, called them tough.
*
Sri Shyama Shastry’s expertise in Taala and Laya is very evident from his treatment of the Misra Chapu Taala.
[In regard to the Taala; Graha or Eduppu denotes the point within the Āvartanam of a Taala, when a composition or stanza in a composition begins. Graha (Eduppu) can be two ways. One is Sama; and, the other is Vishama.
When a song begins at the first beat of a Taala it is Sama. And, when song begins either before or after the stroke of Taala it is Vishama.
Vishama is classified into two, as: (a) Athitha Graha: When the song begins first; and, it is then followed by Taala beat; and, (b) Anagata Graha is when a Taala begins first; and, the song follows it later.]
The Kritis of Sri Shyama Shastry (like those of Sri Dikshitar) do not start on Athitha-Graha. But, this feature occurs within the body of the Kriti, perhaps to satisfy the requirements of prosody. Usually, the Pallavi and, at times, Anu Pallavi of his Kritis commence in Anagata-Graha; while the Anu-Pallavi and Carana begin with Sama-Graha.
For instance; the Kriti ‘Devi nee padasarasa ‘(Kambhoji) commences in Anagata Graha with ‘Pa’ as the Graha-Svara; while, its Carana begins in Sama Graha.
[ It is mentioned that in Patantara – the texts of the Kritis- that came into use after 1930, the construction of the musical elements; especially of the Eduppus changed much ; and the 4+3 format was not maintained throughout.
For instance; in the Kriti ‘Ninnu vina’, the Pallavi is framed as 2+2+3; the Anupallavi ‘Pannaga-bhushannudaina’ and the Carana ‘Parama-lobu-lanu’ are of the usual 2+7 Eduppu; not consistent with the 4+3 formation of the Pallavi.
For more on this issue, please see the extracts from the work of Smt. Sharadambal, given in later in this post]
*
An excellent feature of his Kritis is that the Sahitya is arranged in concordance (Samanvaya) with the Taala–jatis (beats of the rhythm cycles).
Sri Shyama Shastri has used the different combinations of Svara syllables as well as Sahitya syllables to weave new patterns, within the framework of the Taala.
In his compositions, we find many words constituting of five syllables corresponding to the tâd-in-gina-tom in a natural way.
In the compositions as well as in Svara-Sahithya we find words as ‘Anu-dina-mu, Tarunamidi, durusu-ganu, kamala.mukhi, samayamidi and so on.
His compositions have plenty of Sahitya syllables, which are in the same time-units as the Dirgha-svaras and Hrasva-Svarâs, forming different patterns within the Taala structure
*
Another versatile feature in the Kritis of Sri Shyama Shastri, with regard to Taala, is that he has composed Kritis in Taalas and Gatis (sub-divisions of a beat in a composition) that are interchangeable.
He has composed a few Kritis suggestive of two rhythms. Here, one is the inherent rhythm (Sthapita-Taala); and, the other is the suggested rhythm (Suchita-Taala).
For instance; in the Kriti Shankari-Shamkuru (Saveri), Rupaka (1+1) is the Sthapita Taala; and Adi Taala (Tisra-gati, 3) would be the Suchita-Taala. The Pallavi and Anu-Pallavi, at the outset, are in Rupaka Taala; and, the Carana follows the Adi Taala (Tisra-gati).
And, similar is the case with another Kriti, Birana-varalichi’ (Kalyani) , which can be rendered in both Rupaka Taala (Chatursra- gati, 2+4) and also in Adi Taala (Tisra gati-3).

Laya, Taala, Sruti and Kala are intricate concepts in Karnataka Samgita. They are as nebulous as one often flows into another.
Laya is commonly translated as tempo; which is inseparable from rhythm. And, rhythm is the ordered movement in time and space
It is also said; Laya is the pulse of the rhythm, which has three major speeds: Vilamba (slow), Madhyama (medium or normal) and Dhruta (fast).
Thus, Laya is said to include both rhythm and tempo; which are measured by the uniform flow of the time-duration (Kala). With that, Laya is the ordered movement of rhythm in time.
Suffice it to say that Laya could be taken as rhythm.
And, rhythm in our music is two-dimensional; the one that is related to the pitch is termed Shruti-Laya; and, the other related to the time-units is called Taala-Laya.
[Dr S A K Durga explains ‘The Laya stands for the interval of time between the beats and movement in time. Thus the term “Laya” means both rhythm and tempo created by the even measured flow of the uniform duration of Kala (time).
Prof .P.S. Narayanaswami: Rhythm gives stability and form to music. It can be described as the tangible gait of any musical movement. In Carnatic music, this is referred to as Laya. The common fallacy is that rhythm or laya is confined to percussion instruments and the rhythmic patterns produced therein. But laya is not limited to just that. It is present not only in melodic compositions, which usually have a rhythmic metre in an apparent manner but also in the creative aspects, sometimes conspicuously (like in Neraval or Kalpana-svara) and subtly at others (Raga Alapana and Tanam)]
*
Laya, for all its beauty, is abstract. You need a device, which measures and monitors this abstract time-flow. And, that function is performed by Taala.
If Laya is the rhythmical movement, Taala is that which measures the tempo of that movement. So, Laya implies movement; and, it can be perceived when there is a motion.
Taala (derived from the root tada or tadana) signifies a ‘beat’. The time-interval between the beats and its movement could also be taken as Laya, the rhythm.
Taala is the measurement of time-units in our music. And, the degree of speed with which the time-units, in each division of a Taala-cycle, follow each other is termed as Kala.
{But, Kala is also used to indicate Laya; say, as in: Madhyama Kala, Chowka Kala etc.]
The structural units of a Taala are called Angas. Such Angas are of different kinds.
Here, Anu-Dhruta (One Aksharakala) consists only the beat with palm. Dhruta (2 Aksharakala) is a beat followed a waving of hand. Laghu-Dhruta (4+2 Aksharakala) consists beat and finger counts (Laghu+Dhruta). And, Guru-Dhruta (8+2 Aksharakala) is rendered in Dhruva-kala and Patita-(Guru+Dhruta) wave to left and right or circle with thumb-up + beat with palm + turn (wave).



Taala, in turn, is reckoned by the finger counts, beats and wave of the hand. This manner of counting and keeping time is termed as Kriya. And, Kriya is the action of fingers, palms, hands, in order to keep track of the Taala-units.
And, when it is done without making audible sounds, it is called Ni-shabda-Kriya. And, when the beats are counted and played on cymbals etc., it is Sa-shabda-Kriya.
In the execution of a Taala, between two successive Kriyas, there is a period of rest or pause; and, that has to be maintained consistently.
The action of Kriya (manifesting as Taala sequence) and the interval between two elements of Kriya are interrelated. Further, each Kriya is an extension of its previous one. Here, the duration of such time-lag between two Kriyas assumes importance; and, with its increase or decrease, the Laya becomes faster or slower.
*
In Dhruta-Laya (fast), the Kriyas follow each other in quick succession, as the time-lag between them is very short. In Madhya- Laya or medium tempo, the Laya gets doubled; and, a further doubling of laya results in Vilambita laya.
This suggests; an increase in Laya results in decrease of the speed, i.e., the speed or tempo of a piece is inversely proportional to its laya.
*
The tempo of the musical composition in Indian Music is not marked by the composers as Indian music is learnt through oral tradition; and, the composers did not write their compositions with notation, unlike the composers of Western music. In Indian music , the compositions are performed in the tempo according to the Rasa and Bhava of the Raga and Sahitya, besides the performer’s own decision according to her/his concept of aesthetics, in the presentation

Kala-pramana
Smt. Sharadambal observes : regarding the tempo or Kala-pramana of the Compositions:
Though, most of the songs of Shyama Shastry are in slow medium tempo in Adi-Taala, there are some songs in fast and medium tempo.
The songs in Misra-Chapu and Triputa-Taalas also are mostly sung in slow medium tempo. The long drawn out rhythm with many pauses is seen in Chapu-Taala compositions with less number of words; and, with pauses here and there in these Kritis.
Some of his compositions in Adi-Taala have a tight knit relation between the Taala–Aksharas and the Sahitya letters. Almost all the Svara-letters have Sahitya-letters; and , Hrasva letters found in profusion.
For example; songs like’ Sarojadala-netri’ in Shankarabharana Raga; and in ‘Devi Brova’ in Chintamani Raga, though are set in Adi-Taala, the tempo seems to be increased and gives the impression that the song is set in Madhyama-kala. We do not find extensive pauses in these songs. The pauses are limited; and, words are many; and, this makes it appear as though the tempo is increased.
The songs set in Adi, Rupaka and other Taalas are in fast medium tempo. ‘Parvati-ninnu’ in Kalkada, ‘BiranaVaralicci’ in Kalyani can be cited as examples. Thus we find three different tempos such as slow, slow medium and fast medium tempos among the compositions of Shyama Shastri.

Pada-garbha / Arudi
Arudi or Pada-garbha is a pause that occurs in between the Taala- Avartas. Usually it occurs at the middle of the two Kalai Adi Taala or in the beginning of the next Avarta; or in the beginning of the third Avarta; or in Rupaka Taala or Chapu Taala.
The Kritis: ‘Kanaka-shaila’ (Punnagavarali); ‘Mayamma’ (Ahiri), ‘Emani-migula’ (Todi), ‘Palinchu Kamakshi ‘ (Madhyamavathi); ‘Devi-ni-padasarasa’ (Kambhoji); ‘Devi-mina-netri’ (Shankarabharana ); ‘Devi brova’ (Chintamani ), in Adi Taala two Kalai, all have the Pada-garbha exactly at the middle of the Avarta; that is, on the first Druta.
Here, the pause occurs dividing the Avarta into two; and, after a pause for two or four or three Aksharas, the song proceeds further.
In the songs having two Avartas in the Pallavi, the Arudi occurs in both the Avartas. For instance; we find Pada-garghas in the two Avartas in the kriti ‘Mayamma’ (Natakuranji); one in the first Avarta; and, the second in the second Avarta.
Mayam | ma nannu | Brova vam || ma+ ma ha ma | ya …u | ma … ||
Similarly in the song ‘Saroja-dala-netri’ in Shankarabharana Raga, we find two Pada-garbhas for the pallavi
Saroja dala netri Himagiripu | tri … ni | padam
Sada nammina namma subhamim | ma …O Sri
In Adi Taala, this pause occurs at the beginning of the next Avarta as in the song ‘Karuna judu’ in Sri Raga
Karuna judu ninnu | nammina | va-duga ||
da …in ta | parake | lanamma ||
The kriti ‘Karuna-judu’ as rendered in Misra Chapu Taala, in the 4 + 3 gait, has the Pada-garbham at the beginning of the fifth Avarta in the word ‘ga’
*
The Kritis in Rupaka Taala and Chapu Taala have the Pada-garbham at the commencement of the third Avarta.
‘Ninne’ in Todi Raga and Chapu Taala’ has two lines of Sahitya; and; had pause for the two lines at the beginning of the third Avarta
Ninnenam || mi na ……… || nu ……… sa || da ……… ne ||
Vin na pa || mu vi ni || nan …… nu || bro ……vumu ||
The other examples are : ‘Mina-locana’ in Dhanyasi Raga in Chapu-Taala and ‘Nannu-brovu’ in Lalita Raga are in Chapu Taala; ‘Pahi Sri’ in Ânandabhairavi Raga in Rupaka Taala; ‘Karuna juda’ in Varali Raga in Chapu Taala; ‘Birana vara’ in Kalyani Raga in Rupaka Taala; ‘Ninnuvina’ in Ritigaula Raga in Rupaka Taala
*
Pauses found in different places
There are some kritis, in which pauses occur in different places i.e. at the end of the pallavi; or at the end of the first Avarta and so on.
There are kritis which do not have pauses in between the Avartas; but, pause occurs only after finishing the Pallavi at the end of the second Avarta.
For example; in the kriti ‘Durusuga’ in Saveri Raga, we find pause only at the end of the Pallavi, whereas in the kriti ‘Marivere’ in Anandabhairavi Raga, we find a pause at the end of the first Avarta itself in both the lines as
Marive ……| ……………re | ga ti ye vva | ram … ma ||
Mahilo ……| …………….I. | mahilo ….. | brocu taku ||
Similarly in the kriti ‘Janani’ in Saveri Raga we find a pause in the beginning, but after that words follow without any pause up to the end and the pause occurs after the words as :
Janani ………… Nata | jana pari | pa lini …
pahivambhava | ni ……….| …………
*
In some kritis, pauses occur in the beginning; at the end of the Avartas in some; and, in many places in some kritis ; whereas there is no pause at all in some kritis.
The kritis in Chapu Taala are found with fewer words; with more pauses occurring in different places.
In the kriti ‘Talli-ninnu’ in Kalyani Raga in Chapu Taala, a pause occurs at the end of the second Avarta; and, it is continued in the beginning of the third Avarta.
Talli | Ninnu nera | …………… nammi | na nu vino | ve ..
In the kriti ‘Ninnu-vinaga’ in Purvikalyani Raga in Viloma Chapu Taala, we find karvai at the end of the first and third Avarta. The karvai is found in the second line also.
Ninnu vina …… | …… ga mari | dikk-evarun ……| na ……ru ||
In the kriti ‘Brôvavamma’ in Manji Raga ,in Chapu Taala, pauses occur in many ; and, not at specified places.
Brova vam ……|……ma …… ta … | masa me ……| le … ………………| ………….
bi ……..| ra …………na …… || ……
Devita ………|…… la le ………| ne …………bi | ra …… na ……
*
Similar type of kriti is ‘Nilayata-kshi’ in Pharaz Raga. We can find pause here and there controlling the flow of the rhythm.
Ni …… la …… ya || ta ………kshi || ni …… ve …||
jagatsa ……kshi ||
**
In order to control the less number of words employed in an Avarta in the above mentioned kritis in Chapu Taala; Shyama Shastri might have used these pauses wherever necessary.

Aspect of Laya
The advent of the Trinity with their compositions paved the way for a new era in the growth of Kriti. They gave importance not only to melody but also to the temporal aspect or laya.
Eduppu or Graha is the place where in the song starts in the Taala. This plays an important role in the construction of a composition.
There are songs which start on Sama Eduppu; that is, the Taala as well as music start at the same time from the beginning of the Taala count.
There are some songs which start after the Taala begins. This is called Anagata Eduppu.
Some songs start before the Taala Avarta, that is in the previous Avarta itself; and, that is called Atitha Eduppu.
Usually in songs, the Eduppu will uniformly be the same in all the three Angas, either Sama or Anagata
We also find different Eduppus among the different sections within a song of Shyama Shastri.
There are some songs in which two Angas start on the same Eduppu; and, the other Anga has a different Eduppu. They are as follows:
1.Birana – Kalyani – Rupaka
2. Shankari – Saveri – Rupaka
3. Himadrisute – Kalyani – Rupaka
4. Devi-mina-netri – Shankarabharana – Adi
5. Devi-neepada – Khambhoji – Adi
6. Enneramum – Punnagavarali – Adi
7. Mayamma – Natakuranji – Adi
8. Karuna-juda – Varali – Chapu
9. Shankari – Kalyani – Ata
The song ‘Birana Varâlicci’ in Kalyani Raga and the song `Himadrisute’ are with the same structure, but in Sanskrit, a special Eduppu is found in Rupaka Taala
The Pallavi and Anupallavi start after the first beat; that is, in the second beat or after four Akshra kaalas. The Carana of the song start after two Akshara Kaalas.
In this song, the Pada-garbham (Arudi) falls on the sixth beat; and, again the words start after a karvai of eight Aksharas. This gives a grip to the song over the Taala.
Another song in which the Carana alone starts after two Aksharas, while the Pallavi and Anupallavi start on some Eduppu is ‘Shankari’ in Saveri Raga. These two Kritis belong to the group of Kritis prevailing since early thirties.
**
There are some Kritis, which figure only after 1930.
Among them, the two Kritis each in the Ragas Shankarabharana and Kambhoji alone figure in the notation of Shyama Shastri II; and, the rest figure in the books of others of the same period.
In the four Kritis in Adi Taala, mentioned above, either Sama or Anagata Eduppu is kept for one Anga; and, the other two Angas have different ones.
For example, in the song ‘Devi ni pada’ in Kambhoji, the pallavi starts after two Aksharas; while Anupallavi and Carana have Sama Eduppu.
In the kriti ‘Mayamma’ in Natakuranji Raga, this is reversed. Pallavi has Sama Eduppu; and the Anupallavi and Carana start after two Aksharas.
In the Kritis ‘Devi-mina-netri’ in Shankarabharana Raga and ‘Ennçramum’ in Punnagavarali Raga, the Pallavi and Carana start after four Aksharas; while the Anupallavi start on Sama.
In the kriti ‘Karuna juda’ in Varali Raga, Chapu Taala, the Anupallavi alone starts after one Akshara; and, the other two Angas start on Sama
In the kriti ‘Shankari’ in Kalyani raga, Chatushra Atta Taala, the Carana alone start after one Akshara and the others on Sama.
There are some songs set in Misra Chapu Taala in the Krama order as 3+4; but, the Eduppu gives the impression as if the songs are sung in Viloma Chapu.
The songs start in the last beat of the Taala; and so the structure is formed as 2 + 3 + 2. The Kritis ‘Nannu-brovu’ in Lalita Raga and ‘Talli-ninnu’ in Kalyani Raga and ‘Mina-locana’ in Dhanyasi Raga can be cited as examples.
The song ‘Ninnu-vinaga’ in Purvikalyani Raga is the only song set in regular Viloma Chapu , which starts in the place Taka-dimi and then taki-ta follows as in HW of Shyama Shastri II, says S.Rajah.
In the HW of Shyama Shastri II , all the songs are written only in the form 4+3; but, the Eduppu alone is denoted either as 4+3 or 3+4 or 2+3+2 by an asterisk mark.

The Taalas handled by Sri Shyama Shastry
Sri Shyama Shastri has composed Kritis and other compositions in various types of Taalas; such as: Adi, Rupaka, Misra Chapu, Mathya, Triputa, Jhampa and Ata Taala. All the Taalas come under the Sapta- Taala group.
[In the Karnataka Samgita concerts, the four Taalas that are commonly used are – Adi, Rupaka, Misra-Chapu and Khanda-Chapu. And, most number of songs is in Adi Taala.

Adi Taala has several compositions, each in a different tempo and gait. These could be effectively used to bring out contrast within the concert. Variety can also be brought out by singing compositions with different starting points. For example, a composition can start at the very first beat of the Taala. Or it can start at the next beat or after a few counts within the beats. The starting point is known as Eduppu or Graha. – Dr. P S. Narayanaswamy]
As regards the number of compositions in each type of Taala:

Adi Taala
Of the thirty compositions set in Adi Taala, as many as twenty-seven are the Kritis. And the rest three are: a Gita (Santatam-Pharaju); a Varna (Dayanidhe –Begada); and, a Svarajati (Rave Himagiri –Todi).
All the Kritis are of the Eka Kala and Dvi Kala type. The Laya is Vilambita in most cases. Sometimes the Madhya Laya is also used.
Of the thirty compositions in Adi Taala, as many as twenty-three start on Sama Graha; and , seven on Anagata Graha (half Eduppu).
For the three Kritis: Karuna-nidhi-ilalo (Todi); Shankari Shamakuru (Saveri) and Parvathi ninnu ne (Kalgada), the Tisra Gati is employed. In Tisra -Gati, each unit of the Taala will be counted as ‘ta-ki-ta’ (a unit of three Aksharas)
The variation in the Akshara-kala of each count of a Taala (Gati-bedha) is another feature here.
It is said; the compositions in Tisra Gati –Adi- Taala (with a total Akshara kala duration of 24) could also be rendered in Rupaka Taala (12 Akshara kala duration).
Following that; the Tisra Gati Kritis in Todi and Saveri Ragas are sometimes sung to Rupaka Taala.
And in the other way; the Rupaka-Taala-Kritis – Ninnu-vina (Ritigaula) ; Birana Varalichi (Kalyani) ; and , Himadrisute (Kalyani) can also be sung to Tisra-Gati-Adi -Taala.
**
Chapu Taala
It is a very common saying that among the Ragas, the Anandabhairavi; and, among the Taala, the Misra Chapu Taala are the favorites of Sri Shyama Shastry. He did, indeed, pay special attention to these two; and, transformed their modes of presentation.
The Chapu Taala is believed to have originated from the folk tradition; and, it was much used in the Bhagavatamela plays, which Sri Shastry as a youngster loved to watch while his family was Thiruvarur.
The beat (ghata) is the only kind of Kriya used in the Chapu Taala; and, there are no other Angas here such as Dhruta or Laghu etc. And, its Kriyas are not of uniform duration.
The Chapu Taala (which is said to be an abbreviated form of Tisra-Jati-Triputa-Taala) has four variations: Tisra-Chapu (1+2=3) ; Khanda-Chapu (2+3=5); Misra Chapu (3+4=7) ; and, Sankirna-Chapu (4+5=9).
Of these variations, Sri Shyama Shastry adopted the Misra Chapu of seven Akshara kala duration for many of his compositions.
As said; Misra Chapu has two parts. The first part (3) is three-fourths the duration of the second (4). In sum, it would be reckoned as having two beats (3 and 4). But, in practice, it is played in two beats. And, sometimes, instead of the first beat, the Taala would commence with a wave-motion (Visarjita).
Sri Shyama Shastry revised the mode of rendering the Chapu Taala ( 3+4) by reversing the sequence of its beats and transforming it into Viloma Chapu Taala (4+3). And, this became a hallmark of his preferred Taala structures.
The following are the compositions of Sri Shyama Shastry set to Misra Chapu and to Viloma Chapu
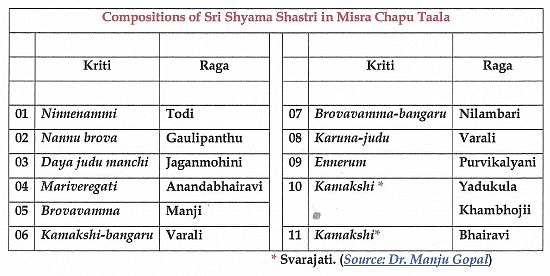
Among the eleven compositions in Misra Chapu Taala, five compositions viz., the two Svarajatis; the two Kritis in Varali; and one Kriti in Anandabhairavi, all start with Sama Graha . And, the rest six, start in Anagata Graha.

Of the seven Kritis in Viloma Chapu Taala, the two Kritis Trilokamata (Pharaju) and Ninnu-vinaga-mari (Purvikalyani) start on the Sama Graha. And, the other five Kritis start on Anagata Graha, on the second beat. [The Kriti Karuna-judu (Sri) is sung by some in Adi Taala.]
**
Triputa Taala
There are nine compositions set in Triputa Taala; and, these include three Gitas.
Of these nine compositions: three Gitas – Kamakshi (Pharaju); Kamakshi (Madhyamavathi); and Sarasakshi (Saveri); as also the three Kritis – Paramukha-melanamma (Kalyani); Palayasumam (Arabhi) and Nilayatakshi (Pharaju) – all start Sama Graha (Eduppu).
The other three Kritis in this group: Nannubrova (Janaranjani); Adinamu-ninchi (Ananadabhairavi) ; and, Ennerum (Punnagavarali) – start on Anagata Graha (half Eduppu).
**
Other Taalas
As regards the compositions in other Taalas

In the case of the Taalas of the twenty compositions, the Akshara value, in each case, amounts to 7 or to multiples of 7.
The Taalas that are involved here are: Tisra-Jati-Triputa (7 Aksharas); Misra Chapu (7 Aksharas); Khanda-Jati-Ata (14 Aksharas); and, Viloma Chapu (7 Aksharas).
Of such twenty compositions, 9 are in Tisra Triputa; 12 in Misra Chapu; 7 in Viloma Chapu; and 2 in Khanda Ata. (Source: Dr. Manju Gopal)
*
Of the 72 known compositions of Sri Shyama Shastri, 47 start with Sama Eduppu; and , 25 compositions with Anagata Eduppu.
Examples of Sama Eduppu are: Emani migula (Todi, Adi Taala); Palayasumam (Arabhi, Triputa Taala); Sari evvaramma (Bhairavi, Khanda Jhampa Taala); and Shankari-Shankari (Kalyani, Khanda Ata Taala).
Examples of Anagata Eduppu are: Palimpavamma (Mukhari , Adi Taala , half Eduppu); Birana Varalichi (Kalyani, Rupaka Taala, Eduppu in the second beat); Nannubrova (Janaranjani, Triputa Taala, half Eduppu); Talli-ninnu (Kalyani, Viloma Chapu- Eduppu on the second beat)
*
Though there are no compositions among Sri Shyama Shastry’s creations, that explicitly commence with Atitha Eduppu, shades of this feature can be noticed in some of his verses. For example, in Mayamma (Ahiri, Adi Taala), the Carana of which reads:
Sarasija-bhava Hari-Hara-nuta sulaita nee/ Pada-pankaja-mula-sthira-mani Nammiti -Nammiti -Nammiti ni
Here, the portion from ‘pada pankaja’ is said to start with the last count of the previous Avarta. This could be taken as Atitha Eduppu.
*
A unique feature of the compositions of Sri Shyama Shastry is the modulation of the rhythm (bigu-sugu), which emphasizes certain notes and stretches them.
Another noticeable feature is the rhythmical improvisations (Laya, Taala) do not in any manner hamper the melody (Dhathu) and the consistency of the Sahitya.
In the Kritis and Svarajatis of Sri Shyama Shastri, the Sahitya phrases and the sequence of rhythmic patterns (Taala Jati) blend harmoniously. The long Sahitya syllables are matched by long (Dheerga) Svaras; and the short ones are in tune with the short (Hrasva) Svaras.
For instance; the sequence of the units of Akshara kala (of three different kinds- 5, 7 and 9) combines well, in each case, with the corresponding flow of the Sahitya.
In each case, the Sahitya segment is broken up into the number of units of its Taala.


We shall talk about the Languages of the Kritis of Sri Shyama Shastry
as also about his other types of Compositions
Continued
In
The Next Part
Sources and References
- Indian Culture, Art and Heritage by Dr. P. K. Agrawal
- Shodhganga chapter Six
- Shodhganga Chapter Seven
- Shodhganga Chapter VI
- Shodhganga Chapter VII
- Shodhganga handle
- A Voyage through Dēśa and Kāla
- Compositions of Shyama Shastri (1762-1827)
- Origin and development of Indian music
- https://archive.org/stream/composers00ragh/composers00ragh_djvu.txt
- https://archive.org/details/composers00ragh/page/46/mode/1up
- Prof. P. Sambamoorthy
- https://ebooks.tirumala.org/downloads/syamasasthri.pdf
- https://www.sangeethapriya.org/tributes/shyamakrishna/dl_krithis.html
- http://www.medieval.org/music/world/carnatic/shyama.html
- http://carnatica.net/special/shyama.pdf
- https://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/173579/11/11_chapter%204.pdf
All images are taken from Internet











 **
** 
 **
**
 **
**
 **
**