
Levels of speech
The various ancient texts speak of the levels of speech, which, generally, are taken to be four. Each School – Grammarians, Mimamsa, Upanishads, Tantra, Yoga, mythology etc – offers its own understanding and explanation of the four levels of speech. These levels are variously explained as the varieties of speech that are said to be spoken either in four regions of the universe; or spoken by divine beings and humans ; or as speech of the humans , animals, birds and creatures . These four are even explained as four levels of consciousness.
For our limited purpose, let us briefly scan through other interpretations, before we discuss the Grammarians’ views and their explanations of the four levels of speech.
***
The Asya-vamiya – sukta (Rig Veda: 1.140- 164) which is one the most philosophical , but rather enigmatic Suktas (hymns) of Rig Veda, ascribed to Rishi Dīrghatamas Aucathya (son of Ucathya ), who was also called as Mamateya (son of Mamata) , mentions about the levels of speech, among many other things.
According to Rishi Dīrghatamas, there are four levels of speech. Only the wise who are well trained, endowed with intelligence and understanding know them all. As for the rest; the three levels remain concealed and motionless. Mortals know only the fourth.
Chatvaari vaak parimitaa padaani / taani vidur braahmaanaa ye manishinaah. Guhaa trini nihita nengayanti / turiyam vaacho manushyaa vadanti. (Rigveda Samhita – 1.164.45)
But, he does not specify what those four levels of speech are.
*
The notion that there are four quarters or four levels of existence ; and of which, only one quarter is within the experience of mortals also appears in the Purusha-sukta (Rig-Veda 10.90.3) ascribed to Rishi Narayana – Paadosya Vishva Bhutaani Tri-Paada-Asya-Amrtam Divi .
There are similar notions with regard to Pranava Om where the three syllables A, Vu, and Ma are normally visible. But it is its fourth element the Anusvara (Brahma-bindu) that leads from being to non-being; and , from the word to the silence beyond it.
svarena samdhayed yogam asvaram bhävayet param asvarena hi bhävena bhävo näbhäva isyate– Brahmabindu Upanishad
*
And, there is also the Turiya paada (Chaturtha or Fourth) the fourth line of the Gayatri mantra. It is said; while the traditional three lines of Gayatri mantra can be grasped by reason, the fourth line, which is mystical in its import, and can be comprehended only through intuition. The fourth line (Turiya paada) which reads ‘paro rajas ya tapati’ is said to be hidden (darshatasya) or un-manifest (apad); beyond intellect; resplendent, shining beyond the worlds known; and , which is the support of the Gayatri itself and of the Universe.
This Turiya paada which reads ‘paro rajas ya tapati’ (the pada-pata of which is: ‘Parah- rajase- asau – adhah – maa – praapta – iti’) is, by itself, considered a maha-mantra. Its Rishi is Vimala; its chhandas is Turiya; its Devata is Paramatma; and, its objective (viniyoga) is liberation (moksha).
Asya sree darshatasya Gayatri-turiya paada-maha- mantrasya; Vimala Rishihi; Turiya chhandaha/Paramatma Devata; Moksha viniyogaha /
The Upanishad adores the fourth line as ‘Namaste turiyaaya darshataya padaaya’.
tasyā upasthānam | gāyatry asy ekapadī dvipadī tripadī catuṣpadi | apad asi |
na hi padyase | namas te turīyāya darśatāya padāya parorajase | asāv ado mā prāpad iti ||| BrhUp_5,14.7 ||
*
That idea of four quarters is extended to speech as well. The texts of several traditions speak of four levels of speech. For instance :
The Maitrayaniya (Maitri) Upanishad (1, 11.5), of Krishna Yajur-Veda, mentions the four quarters of speech as those belonging: to the upper region – the heavens (Divi); to the intermediate space (Antariksha); and, to the region of earth (Prithvi) as spoken by the humans (Manusi); and, to the animals (Pashu)
– vāk sṛṣṭā caturdhā vyabhavad eṣu lokeṣu trīṇi turīyāṇi paśuṣu turīyaṃ yā pṛthivyāṃ sāgnau sā rathantare yāntarikṣe.
The Atmavadins (mainly those belonging to Nyaya and Vaisesika Schools) say: the four fold speech can be found in the animals; in musical instruments (such a flute); in the beasts ; and, in the individuals (Atmani)
– pasusu tunavesu mrgesu atmani ca iti atmavadinah
The Satapatha Brahmana (1.3.16) categorizes the speech into four kinds: as that of the humans; of animals and birds (vayamsi); of reptiles (snakes); and, of small creeping things (kshudram sarisrpam)
– varṣā vā iḍa iti hi varṣā iḍo yadidaṃ kṣudraṃ sarīsṛpaṃ 1.5.3.11
Similarly, those who believe in myths and legends say that – the serpents; birds; evil creatures; as also the humans in their dealings with the rest of the world – all use speech of their own.
Sarpanam vagvayasam ksudrasarispasya ca caturthi vyavaharika-ityaitihasikah
The Jaiminiya-Upanishad-Brahmana (1.40.1) deals with the four levels of speech in a little more detail. In a verse that is almost identical to the one appearing in Rig-Veda Samhita – 1.164.45, it mentions that the discriminating wise know of four quarters of speech. Three of these remain hidden; while the fourth is what people ordinarily speak.
Chatvaari vaak parimitaa padaani / taani vidur braahmaanaa ye manishinaah. Guhaa trini nihita nengayanti / turiyam vaacho manushyaa vadanti //
Then, the text goes on to explain that of the four quarters of speech: mind is a quarter, sight is another quarter, hearing is the third quarter; and, speech itself is the fourth quarter.
tasya etasyai vaco manah padas caksuh padas srotram pado vag eca caturtah padah
Further, it says: what he thinks with the mind, that he speaks with speech; what he sees with the sight, that he speaks with the speech; and, what he hears with hearing, that he speaks with speech.
tad yad vai manasa dyayanti tad vaco vadati; yac caksus pasyati tad vaca vadati; yac srotrena srunoti tad vaco vadati/
Thus, finally, all activities of senses unite (Sam) into speech. Therefore speech is the Saman.
Nageshabhatta (Ca. between 1670 and 1750), in his commentary on Patanjali’s Mahabhashya, accepts the four forms of Vac; and, explains the expression ‘Catvari padjatani namakhyato-upasargani-patah ‘as referring to Para, Pashyanti, Madhyama and Vaikhari :
“Bhashya padajatani Para-Pashyanti-Madhyama- Vaikhari rupani / ata evagre nipatah ceti cakarah sangacchate “
*
In the later Upanishads, speech is said to be assimilated with consciousness. The four divisions of speech are explained as four states of consciousness. For instance; Sri Gauda-Paada, the Parama-Guru of Sri Sankara (the teacher of his teacher) , in his celebrated commentary (Gaudapada-karika) on the Mandukya Upanishad while explaining his concept of Asparsha Yoga or pure knowledge, identifies the four levels of speech with the four states of consciousness : Vishva or Vaisvanara in wakeful state (Jagrat); Taijasa in dream state (Svapna); Prajna in deep-sleep (Shushupti); and, Pranava AUM with Turiya, the fourth, the Absolute state which transcends all the three states and represents Ultimate Reality .
sthūlaṃ tarpayate viśvaṃ praviviktaṃ tu taijasam / ānandaś ca tathā prājñaṃ tridhā tṛptiṃ nibodhata // MandUpK_1.4 // svapnanidrāyutāv ādyau prājñas tv asvapnanidrayā / na nidrāṃ naiva ca svapnaṃ turye paśyanti niścitaḥ // MandUpK_1.14 // praṇavaṃ hīśvaraṃ vidyāt sarvasya hṛdi saṃsthitam / sarvavyāpinam oṃkāraṃ matvā dhīro na śocati // MandUpK_1.28 //

Explanations offered by Sri Sayana
Sri Sayana in his Rg-Bhashya deals with the subject of four levels of speech in a little more detail. He says, people use speech in a variety of ways to fulfil their roles and responsibilities in life. And, similarly, the animals, birds, creatures and objects in nature do use their own sort of speech to serve their needs. He then , while explaining these four levels or quarters of speech (ani tani catwari itya atra bahavah) , remarks that each School offers explanations (bahudha varnayanti ) according to its own tenets (sva- sva-mantanu-rodhena). He, next, briefly mentions what those explanations are:
: – According to Vedantins, the four levels of speech could be the Pranava (Aum) – which is the sum and substance of all the Vedic terms (sarva-vaidika-vag-jalasaya), followed by three Vyahritis (Bhu, Bhuh and Suvah). Thus the Pranava along with three Vyahritis form the four quarters of speech.
: – According to Nirukta (Etymology), the language of the three Vedas (Rik, Yajus and Saman ) and the speech commonly used for dealings in the world , together make the four quarters of speech – (Rg-yajuh-samani-caturdhi vyavharikiti nairuktah – 13,8 )
: – The four levels of speech could also be related to four regions representing four deities : on the Earth as Agni (yo prthivyam sa-agnau); in the mid-air as Vayu (Ya-antarikshe sa vayau); and, in the upper regions as Aditya (Ya divi saditye). And, whatever that remains and transcends the other three is in Brahman (Tasya-mad-brahmana).
: – The speech, though it is truly indivisible, is measured out or analyzed in the Grammar as of four kinds or four parts-of-speech (akhandayah krtsnaya vacah caturvidha vyakrtattvat). Accordingly, the four divisions of speech are named by the followers of the various Schools of Grammar (vyakarana-matanus-arino) as: Naaman (Nouns), Akhyata (Verbs), Upasarga (prepositions or prefixes) and Nipata (particles)
:- According to the wise who are capable of exercising control over their mind; the Yogis who have realized Sabdabrahman; and, others of the Mantra (Tantra) School, these four levels of speech (Evam catvari vacah padani parimitani) are classified as : Para, Pashyanti, Madhyama and Vaikhari.
Manisinah manasah svaminah svadhinamanaska brahmana vacyasya sabdabrahmani dhigantaro yoginah paradicatvari padani viduh jananti
Apare mantrkah parkarantarena pratipadanti Para, Pasyanti, Madhyama Vaikhariti catvariti

The power of the spoken word
In the Indian traditions, it is believed that it is only in its oral form that the language becomes fully alive and reveals its true nature , provided it is spoken properly. For Indian thinkers, language was primarily the spoken word or speaking itself (vac); while the written word, as a secondary aid, was only a coded-representation of the spoken word; but, without its nuances. Perhaps the most salient feature of ancient Indian linguistic culture was its concern for preserving the purity of the spoken word.
It was the speech, the spoken word not the written letter that is at the base of the Sanskrit grammar. All speculations and practices are concerned with the oral. Panini’s Astadhyayi is also based on the sounds of spoken Sanskrit. The spoken language in Sanskrit was/is the real language.
Therefore, right from the earliest period, the study of speech has been one of the major concerns of various Schools of Indian traditions. The power of the spoken word or still more of the potent un-spoken sound was well recognized.

Levels of awareness and speech
The notion of various levels of awareness and speech is accepted and discussed in almost all the Schools of Indian philosophy and Grammar. Although numerous meanings are read into the term catvari vak (four kinds or levels of speech), the one that is commonly understood and commented upon by most Grammarians and philosophers is the classification of speech into four strata: Para; Pashyanti; Madhyama; and, Vaikhari.
The entire system of such classification is rooted in the faith that at the top of this language hierarchy, there is only One-indivisible (ekameva) Reality; and, it transforms itself (Vivarta), manifests itself , resulting (Parinama) in variety of sounds, word, sentence etc.
The theory underlying the evolution of speech is an extension of that faith; and it asserts, though there are several levels in the hierarchy of language, they all emanate from one indivisible reality Sabdabrahman. And again, the Sabdabrahman is identified with Para Brahman, the Absolute.
The principle that is involved here is also based in the dictum that diversity essentially pre-supposes an underlying unity (abedha-purvaka hi bhedah). In other words, it says, where there is difference or division there must be a fundamental identity underneath it ; else, each cannot relate to the other; and , each object in the world would be independent of , or unconnected to every other thing in existence.
This concept provides the foundation for treating all forms of speech as emanating from a single source. The various levels of language from the most subtle to the gross are, therefore, treated as hierarchy or the levels of a unitary language-system. Most of the philosophical speculations on the process of manifestation of language; and, the discussions upon its various stages – from the subtlest (Para) to the most explicit (Vaikhari) – are based in that principle.

Grammarians’ view
Each of the major schools of Indian philosophy and Grammar tried to explain the origin and nature of the Universe by exploring the nature and manifestations of the sound. They built elaborate philosophical edifices around the concepts they evolved during that process. Those traditions considered sound as one of the most important principles of existence; as the source of matter ; and , also the key to be free from it. They described Sound as the thread-like link connecting the material and spiritual realms.
The analysis of the speech by the Grammarians is not merely an intellectual exercise, but is also a philosophical quest in an attempt to identify all forms of speech as originating from Sabda-Brahman, the ultimate ground of all speech phenomena. The study of Grammar was itself looked upon as a means or as a right-royal-path to liberation (moksha-manamam ajihma raja-paddhatih).
*
Speech was regarded as the verbal expression of a thought that arises in a person’s consciousness. If there is no consciousness, there would be no speech. Speech (Vac) is indeed an outward form of consciousness (chetana). Vac is the word principle that gives expression to the latent or unmanifest thoughts and feelings.
That was meant to say; thinking is, in fact, a sort of internal speaking. Such inaudible speech was regarded the seed or the potent form of explicit speech that is heard by others. It was also said; all knowledge is interpreted in terms of words; and, it is quite not possible to have any sort of cognition that is free from words (tasmād arthavidhāḥ sarvāḥ śabdam-ātrāsu niśritāḥ– Vakyapadiya: 1.123)
The process of transformation of a thought or an impulse arising in ones consciousness into a cognizable, explicit speech is said to resemble the evolution of the Universe from the un-manifest (A-vyakta) to the manifest (Vyakta) material world.
Such process of unfolding is said to take place, at least, in two stages. The first one is the thought that flashes and takes a form within. And, the other is that which comes out as audible speech riding the vehicle of words and sentences; attempting to convey the idea that arose within. The former is intuition that springs up; and, the latter is the effort that is exerted, both internally and externally, to put it out.
Here, the latent, unspoken form of thought that instinctively springs up and is visualised, within one’s self, is called Pashyanti Vak (thought visualized). The Pashyanti, which also suggests the visual image of the word, is indivisible and without inner-sequence; in the sense, that the origin and destination of speech are one. Here, the ‘internal speech’ or ‘thought’ stands for what is intended to be conveyed. That intention is instinctive (prathibha) and immediate; and, it does not involve stages such as: analysis, speculation, drawing inferences and so on. At the level of Pashyanti Vak, there is no distinction between word and meaning. And, there is also no temporal sequence.
The Pashyanti Vak thereafter transforms into an intellectual process, the level of thought (Buddhi), during which the speaker looks for and identifies appropriate words, phrases, and their sequence, which are capable of conveying his intention candidly. That sequence of thoughts results in definite and clear array of words. As that cognition arises and takes a form within, he grasps it. This is the intermediate stage – The Madhyama vak, a sequenced but a pre-vocal thought – described as the voice of silence; perhaps best understood as internal speaking. Here, there is no perceptible sound (Nada). The Madhyama vak is in an inaudible wave or vibratory (spandana) form.
And, the Madhyama, when it is put out explicitly through uttered words and sentences; and, when it comes out of the speaker’s mouth in sequenced and verbalized speech-form, it is called Vaikhari Vak. For the purpose of putting out the Vaikhari Vac, the speaker employs a sentence comprising words uttered in a sequence. The word itself comprises letters or syllables (varnas) that follow one after the other in space and time.
Thus, the Vaikhari is the articulated speech, which, as sound waves, reaches the ears of the listener and then on to her/his intellect. The Vaikhari is the physical or gross form of the subtle thought or is the outward expression of the intention of the speaker. And, when it emerges as the spoken-word, it is the one that is heard and apprehended by the listener, in a flash of understanding (Sphota).
[The process of Hearing, that is what is heard and grasped by the listener, of course, operates in the reverse direction.]
The spoken word comes out of one’s mouth, no doubt. However, it needs the assistance of breath and of several body parts in order to manifest itself (Vikhara literally means body; and, Vaikhari is that which employs bodily organs). The head, throat, tongue, palate, teeth, lips, nose, root of the tongue and bosom are said to be the eight places which assist the sounds of the letters to become audible and explicit.
When a person wills to express a thought orally, the air (Prana) inside his body spurs and moves up (Ut-chara). Sabda or the Vac (speech or utterance) then manifests through Dhvani (sound patterns), with the assistance of appropriate organs.
[The King Pratardana of Kasi (Kasi-rajah-Pratardanaha – prātardanam-amtaram agnihotra mityācakṣate), in the Kausitaki Brahmana Upanishad, makes an interesting observation that one cannot breathe and speak at the same time (‘when a man speaks he cannot breathe; and when he breaths he cannot speak’- kau.Up.2.5).
Yavadvai purusho bhasate na tavat-pranitum shaknoti pranam tadā vāci juhoti …. Yavadvai purushah praniti na tavat-bhashitum shaknoti vacam tadā prāṇe juhotyete – kauṣītaki brāhmaṇao upaniṣat .2.5]
***
Thus, the transformation of a thought into spoken-words involves two kinds of effort: the internal process (abhyantara prayatna) and the external effort (bahya prayatna). The former is classified into two kinds (Pashyanti and Madhyama), while the latter (the external) is said to be of eleven kinds.
And, of the three levels or stages of speech, Pashyanti is regarded the subtle forms of Vac; while Madhyama and Vaikhari are its gross forms.
The chief characteristic of Vaikhari Vak is that it has a fully developed temporal sequence. At this level, the speaker’s individual peculiarities (such as accent, voice modulation etc) are present, along with relevant parts of speech. Though the Vaikhari gives expression to subtler forms of Vac, it is not considered as the’ ultimate’.
*
The ancient Grammarians went to great lengths, systematically, to trace the origination of each letter, its appropriate sound; the intricacies and efforts involved in producing them. (Please see the Note * below)
*
[* In the Sanskrit, the vowels and consonants sounds are classified and arranged dependent on their origin (pronunciation) in different parts of mouth, such as throat, palate, teeth or lips.
The vowels and consonants are so arranged that those emanating from the throat come first. These are followed by those pronounced through tongue; the palate; teeth and the lips. All sounds are arranged as those from the inside of the mouth proceeding outwards, in that order. No other ancient system of writing seems to have been so systematically thought out.
The vowels (Svara-s) , alternating long and short, come first : अ (a) आ (aa) इ(i) ई(ee) उ(u) ऊ (oo) ऋ (r) ॠ (r) लृ (lr) ए (e) ऐ (ai) ओ (o) and औ (au)
The commencing vowels अ (a) and आ (aa) are pronounced in the throat – Kantya (कण्ठ्य).
They are followed by vowels इ(i) and ई(ee) produced by the tongue touching the base of the teeth , Taalavya (तालव्य).
The vowels उ (u) and ऊ (oo) are produced using the lips making a rounded opening – Oshtya (ओष्ठ्य).
The vowels ऋ(r) and ॠ(r) are produced by the tip of the tongue curling back against the roof of the mouth- Murdhanya (मूर्धन्य).
The vowel लृ(lr) is produced by the tongue touching the upper teeth – Dantya (दंत्य).
The vowels ए (e) and ऐ (ai) are produced near the throat by the tongue touching the bottom of the teeth and sucking in the air – Kanta-taalavya (कंटतालव्य).
The vowels ओ (o) and औ (au) produced near the throat by the rounding of the lips are called Kantoshtya (कंटोष्ठ्य).
The two ornamental nasal (Anusvara) letters अं (am) and अः (aha ) ,which are used to decorate the vowels, are called the Visarga , meaning sending forth . These sounds, which are neither consonants nor vowels, add a softening short burst effect at the end. These are usually listed as a part of the vowel -group; but are shown at the end.
*
Similar is the emanation of the consonants – from throat outwards to the lips .
The set of consonants – क (ka) , ख (kha) , ग (ga) , घ (gha) , and ङ( nga) – are guttural (throaty) consonants – Kantya (कण्ठ्य).
Then the consonants – च (cha) , छ (chha) , ज (ja) , झ (jha) , and ञ (nja)- are pronounced on the palate- Taalavya (तालव्य).
The next set of consonants – ट (ta) ,ठ (tha) , ड (da) , ढ (dha) and ण( na) – is produced by the tip of the tongue curling back against the roof of the mouth- Murdhanya (मूर्धन्य).
Next are those on the teeth (दन्त्य), like – त (ta) , थ(tha) , द (da) , ध (dha) and न (na) .
And last come those on the lips प (pa) फ (pha) ब(ba) भ (bha) and म ( ma) – (ओष्ठ्य). Oshtya (ओष्ठ्य).
The list is rounded off with semi-consonants like – य (ya) , र (ra) , ल (la) and व(va) ; and the aspirated and sibilant sounds like श (sha) ष (sha) , स (sh) and ह (ha ).
Such unique organization of the alphabet underlines the attention paid to the patterns of articulated sound; points of its location; and , to degree of resonance, in a way that has not been attempted in any other language]
****
[ Abhinavagupta offers a mystic explanation of the arrangement of the Sanskrit alphabets, which are placed in between A and Ha. According to him, in the Sanskrit alphabet, the very first letter A stands for Shiva, the primal source of all existence. A is the initial emergence of all the other letters; and hence is Anuttara, the absolute. And, A not only represents the origin of the language; but, also the expansion of consciousness.
If A the first letter represents Shiva the transcendent source, then Ha the final letter of the alphabet represents the point of completion when all the letters have emerged. If A is Shiva, Ha the last letter is Shakthi, His cosmic outpouring that flows back into Him.
Again, the vowels (Bija – the seed) are identified with Shiva; and, the consonants are Yoni identified with Shakthi. The intertwined vowels and consonants in a language are thus the union of Shiva and Shakthi.
Thus, the sequence of A to Ha contains within itself not only all the letters of the Alphabets, but also every phase of consciousness, both transcendental and universal.
The entire sequence of alphabets, according to Abhinavagupta, represents the state in which all the elements of experience, in the inner and the outer worlds, are fully displayed.]

Philosophers’ view
In the ancient traditions of India, the Grammar, the philosophy of Grammar and the Philosophy run into one another. At times, it is hard to separate them.
While the Grammarians, generally, speak about three levels of speech, the philosophers identify four levels or stages of speech (Vac): Para, Pashyanti, Madhyama and Vaikhari. Of these four forms of Vac, Para and Pashyanti are the subtle forms of Vac; while Madhyama and Vaikhari are its gross forms.
The explanations of the Pashyanti, Madhyama and Vaikhari are almost the same as offered by the Grammarians; however, their interpretations and connotations differ slightly.
*
It is said; the sound has four divisions: Para manifested in Prana (vital energy); Pashyanti manifested in the mind (Manas); Madhyama manifested in the senses (Indriyani); and, Vaikhari manifested in articulate expressions (Vac).
Para Vac is the ultimate and unmanifest principle of speech, the Sabda-tattva (Sabdasya tattvam or Sabda eva tattvam), where there is no subject-object distinction; and, is of the nature of the Absolute (vag vai Brahmeti).
Para vac is identified with Pranava (Aum), the primordial speech-sound from which all forms of speech emanated. It transforms or manifests (Vivarta or parinama) as all forms of sounds, speech etc.
*
According to Abhinavagupta, word is a symbol. The four stage of Vac: Para, Pashyanti, Madhyama and Vaikhari represent its four phases of evolution and also of absorption; the ascent or descent from the undifferentiated to the gross.
It is explained; Para Vac as Sabda-Brahman is the creative energy (Shakthi) that brings forth all existence. It is also the consciousness (chit, samvid), vital energy (prana shakthi) that vibrates (spanda) and enlivens.
While Para Vac is pure consciousness; the three other forms are its transformations. The three lower forms of speech viz. Pashyanti, Madhyama and Vaikhari which correspond to intention, formulation and expression are said to represent ts powers , such as : iccha-shakthi (power of intent or will) , jnana-shakthi (power of knowledge) and the power of becoming (bhuti sakti) or the power of action (Kriya shakthi ). Thus, out of the transcendent Para, the three phases of its power (Shakthi) emanate.
The urge to communicate or the spontaneous evolution of Para into Pashyanti, Madhyama and Vaikhari epitomizes the Cosmic act of One becoming many; and, the subtle energy transforming into a less- subtle matter.
Thus, the speech, each time it emanates, is an enactment, in miniature, of the unfolding (Vimarsa) of the One into many. And each time, when that speech is grasped by the listener and each time it merges into her/his intellect, it re-enacts the process of absorption (Samhara) of the many into One.
The process of manifestation of speech is, thus, compared to the evolution of the Universe. And, that process is said to take place in four stages. First, in the undifferentiated substratum of thought, an intention appears. This first impulse, the self-radiant consciousness is Para-vac (the voice beyond). This latent, un-spoken, un-manifest, silent thought (Para) unfolds itself in the next three stages as Pashyanti (thought visualized), Madhyama (intermediate) and as Vaikhari (explicit) speech).
In its second stage, the subtle thought visualised (pashyanthi-vak) is yet to acquire a verbal form. It is the first sprout of an invisible seed (Bija); and, is the second stage in the manifestation of thought or intention. Then the potential sound, the vehicle of the thought, materializes finding words suitable to express the idea. This transformation of thought into words, in the silence of the mind (Buddhi), is the third or the intermediate stage of Vac (Madhyama-vak). From this non-vocal or un-voiced thought, emerges the fourth stage – the audible sound patterns. It is in that fourth stage, the ideas acquire cognizable forms of speech; and, are transmitted through articulated audible syllables (vaikhari-vak). These four stages are the four forms of the speech.

Tantra
The three- Pashyanthi, Madhyama and Vaikhari – are construed as the three sides of the triangle at the centre of which is the dot-point (Bindu) representing the undifferentiated notion of Para-Vak. The triangle with the Bindu at its centre suggests the idea of Isvara the divinity conceived as non-dual Shiva-Shakti.

In the traditions of Tantra, the process of evolution of the principle of speech (Sabda Brahman) from its most subtle and soundless state of sound – consciousness (Para), in successive stages, into the gross physical speech (Vaikhari) is explained through the principle underling the structure of Sri Chakra.

Sri Yantra is a ‘Cosmogram’ – a graphic representation of the processes of evolution (Sristi) of the Universe emanating from its core; and, re-absorption (Samhara) of the created existence back into itself. And, at the very core or the center of the Sri Chakra is the Bindu, the dimensionless point about to expand immensely. The Bindu denotes what is hidden; the subtle and the most sensitive.
It is said; the true nature of the Supreme Goddess is beyond mind and matter. She is limitless and formless. She is Arupa. But, when She takes a form, the Bindu is her intense representation. The Bindu symbolizes Her most subtle micro form as the Universal Mother, womb, yoni, creator, retainer as also the receiver of the created universe. It is this Bindu that is, in reality, the Sri Chakra; and, everything else is an expansion and manifestation of its aspects.
The Sri Vidya texts call the Bindu also as Sarva-ananda-maya (all blissful); and, the transcendental power (Para Shakthi). It denotes the absolute harmony (saamarasya) between Shiva and Shakthi; as the immense potential of the non-dual Shiva-Shakthi, the union of Purusha and Prakriti.
The evolution (shristi) from the primary state into the mundane level is said to be the apparent separation of Shiva and Shakthi (avarohana karma). And, the reverse process of re-absorption or withdrawal from the gross to the very subtle state is termed Samhara karma.
According to Sri Vidya ideology, in the process of evolution (Vimarsa), that is in the process of shristi or the outward movement or descending arc of creative activity, the speech proceeds from the creative consciousness pulsations (spanda) of the Devi as Para-Vac, the most subtle and silent form of speech-consciousness. And, in successive stages or forms, it moves on to more cognizable forms as : Pashyanti (Vak-shakthi, going forth as seeing, ready to create in which there is no difference between Vachya– object and Vachaka-word); Madhyama (the speech in its subtle form as existing in the anthahkarana prior to manifestation); and, Vaikhari (as articulated gross physical speech).
If the Bindu represents the Para-Vac, its immediate expanded form, the triangle formed by three points, represents the Pashyanti, the second stage of the sound (Nada). The enclosure next to this, the eight sided figure (ashta kona chakra) is the Madhyama or the third stage in the development of sound. The rest of the Chakra represents the physical or the phenomenal stage, the Vaikhari, which is the manifest and articulate form of sound. The Vaikhari form is represented by the fifty letters of the alphabet, called Matrka-s or the source of all transactions and existence.
Thus, in the process of Sristi, in the outward movement from the centre of Reality to the periphery, from the most sublime to the ordinary, the Para assumes different forms, in successive stages. All these four forms, apparently different, are indeed the manifestations of Para Vac which pervades the entire structure of speech and consciousness, in all their levels – from the highest to the lowest; and, it transforms (Vivarta) projects itself in various forms (Parinama).
(Abhinavagupta treats these aspects in a very elaborate manner. We shall talk about the explanations provided by Abhinavagupta and Bhartrhari in the next part.)

Mantra
The Tantra explains the concept of Mantra and Japa in a similar manner.
Mantra is said to connect, in a very special way, the objective and subjective aspects of reality. The Mantra, in its sublime form, is rooted in pure consciousness. The Shaiva text Shiva Sutra describes Mantras as the unity of Vac and consciousness: Vac chittam (Shiva Sutra: 2.1). It is the living sound, transcending beyond the mental plane; the indistinct or undefined speech (anirukta) having immense potential. In its next stage, it unites harmoniously with the mind. Here, it is union of mind (Manas) and word (Vac). That is followed by the Mantra repeated in the silence of one’s heart (tushnim). The silent form of mantra is said to be superior to the whispered (upamasu) utterance.
[When one utters a deity’s Mantra, one is not naming the deity, but is evoking its power as a means to open oneself to it. It is said; mantra gives expression to the identity of the name (abhidana) with the object of contemplation (abhideya). Therefore, some describe mantra as a catalyst that’ allows the potential to become a reality’. It is both the means (upaya) and the end (upeya).]
The reverse is said to be the process of Japa (reciting or muttering the mantra). It moves from Vaikhari through Madhyama towards Pashyanti and ideally, and in very cases, to Para vak.

Ordinarily, Japa starts in Vaikhari form (vocal, muttering). The efficacy of the Japa does depend on the will, the dedication and the attentiveness of the person performing the Japa. After long years of constant practice, done with devotion and commitment, an extraordinary thing happens. Now, the Japa no longer depends on the will or the state of activity of the practitioner. It seeps into his consciousness; and, it goes on automatically, ceaselessly and inwardly without any effort of the person, whether he is awake or asleep. Such instinctive and continuous recitation is called Ajapa-japa. When this proceeds for a long-time, it is said; the consciousness moves upward (uccharana) and becomes one with the object of her or his devotion.
[The term Ajapa-japa is also explained in another manner. A person exhales with the sound ‘Sa’; and, she/he inhales with the sound ‘Ha’. This virtually becomes Ham-sa mantra ( I am He; I am Shiva). A person is said to inhale and exhale 21,600 times during a day and night. Thus, the Hamsa mantra is repeated (Japa) by everyone, each day, continuously, spontaneously without any effort, with every round of breathing in and out. And, this also is called Ajapa-japa.]

Yoga
The system of Yoga also accepts and speaks in terms of Para, Pashyanti, Madhyama and Vaikhari. Here, those terms are meant to denote different sounds (Nada) or the stages of consciousness. It is explained:
: – Para is the most subtle form of sound, not audible; and, in its un-manifest (Avyakta) form resides as Nada at the base (Karana-bindu) in the centre of the Muladhara-chakra, solar plexus (Ekaiva nadatmika vak muladharadudita sati Para ityucyate)

: – And, with the ascent of Prana (vital energy) it moves up to Manipuraka-chakra in the region of navel; and, it is transformed to Pashyanti when it enters the heart-region (hradayakhya) and becomes visible to the Yogis (hradayakhya udiyamanatvat)

The Pashyanti (radiant) stage is compared to a well nourished seed (Bija) which sprouts into two leaves. it, then, acquires the qualities of subtle sound ( which is not audible to the physical ear) , and hue of colour (varna) which can be seen (Pashyan).
: – The Pashyanti, moving up and enters the mind (Buddhi) with a desire or the urge to express itself (Saiva buddhim gata vivaksam prapta madhyama ityucyate). And, on reaching the Anahata–chakra in the region of the heart, it is transformed into Madhyama Vac. Anahata literally means un-struck. Here; the subtle sound (Nada) at the level of the mind is like ‘internal-speech’ which is heard, internally, by the Yogi.

[It is said; the Vac which sprouts in Para gives forth leaves in Pashyanti; buds forth in Madhyama; and, it blossoms in Vaikhari.]
: – When the Madhyama moves up further from heart-region to throat, tongue and mouth it becomes articulate (Vyakta) sound, clearly audible to the external ear at the Vishudhi -chakra. This is Vaikhari, the last stage of sound or speech when it emerges out of the mouth with the help of syllables, words etc and is heard by the listener. And, Vaikhari is the intended speech that comes out clearly through the mouth with the assistance of tongue, lips, teeth and the breath

(Atha yada saiva vaktre sthita talvosthadivyaparena bahirnirgacchati tada vaikhari ityuchyate)
Nageshabhatta in his Parama-laghu-manjusha also describes the four forms of Vac (Para-Pashyanti-Madhyama- Vaikhari), in terms of the Yoga, as those arising from Muladhara, Nabi (navel); Hridaya (heart region) and Kanta (throat)
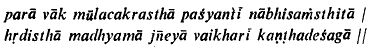

Other explanations
Various other interpretations are also imposed on these four terms.
It is said; Para represents transcendental consciousness; Pashyanti the intellectual consciousness; Madhyama the cerebral consciousness; and, Vaikhari the physical consciousness.
Further, these levels of consciousness are said to correspond with varying levels of awareness: Turia (the fourth, the transcendental or the one-beyond); Shushupti (deep sleep); Svapna (dream state) ; and Jagrat ( wakeful state) , in that order.
And again, these states of consciousness are said to relate to different states of being (bodies). Para which is referred to as the Supreme form; the first form; the pure and resplendent Highest-light etc, is indeed beyond all forms (Turiya); and it is formless. The sphere of consciousness at Pashyanti is said to be the causal body (Karana-sarira); at Madhyama, the subtle or psychic body (Sukshma-sarira); and at Vaikhari, the physical body (Sthula-sarira).
While Para is pure consciousness, the other three are said to be its powers through which it differentiates as its power of will (iccha shakthi) at the subtle level of Pashyanti; as the power of discrimination or knowledge (Jnana shakthi) at the mental level of Madhyama; and, as its power of action (Kriya Shakthi) at the physical level of Vaikhari.
**
In the next part, let’s talk about the theories expounded and the explanations offered by two of the great thinkers – Abhinavagupta and Bhartrhari- on the subject.

Continued
In
The next part
Sources and References
http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/57870/2/02_abstract.pdf
http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/69217/7/07_chapter%201.pdf
http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/57870/7/07_chapter%202.pdf
http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/66674/10/10_chapter%203.pdf
http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/57870/10/10_chapter%205.pdf
http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/116523/13/13_chapter%205.pdf
http://www.svabhinava.org/hinducivilization/AlfredCollins/RigVedaCulture_ch07.pdf
http://www.vedavid.org/diss/dissnew4.html#168
http://www.vedavid.org/diss/dissnew5.html#246
Ritam “The Word in the Rig-Veda and in Sri Aurobindo’s epic poem Savitri
http://incarnateword.in/sabcl/10/saraswati-and-her-consorts#p17-p18
.Vedic river and Hindu civilization; edited by Dr. S. Kalyanaraman
Original Sanskrit Texts on the Origin and History of the People of India…Edited by John Muir
Devata Rupa-Mala(Part Two) by Prof. SK Ramachandra Rao
The Philosophy of the Grammarians, Volume 5 edited by Harold G. Coward, K. Kunjunni Raja, Karl H
ALL IMAGES ARE TAKEN FROM INTERNET
Mohana Bhardwaj
May 13, 2017 at 5:00 pm
Namaskara ! Respected Sir,
The In depth information that you have detailed is enormously useful and helpful in learning PARA VIDYE. I have to read and write several times to learn SARVAM BRAHMA.
Thank You Very Much.
sreenivasaraos
May 13, 2017 at 5:22 pm
Thank you Dear Mohana for the visit and the appreciation.
Please do read articles on other subjects as well
Regards
DKM Kartha
May 14, 2017 at 2:07 pm
namastE,
I have a question that has puzzled me for many years. As I understand it, there has been a long-standing, logically provable belief in India that a WORD and its MEANING are inseparable. If we extend that idea to a poem, we can safely say that a poem’s meaning and its verbal form are integrally connected. MahAkavi KALidAsa put it succinctly: vAgaRttHAviva sampR^ktau…..
When did we in India start believing that the two can be separated? For instance, in my own mother tongue, MalayALam, a great poet showed the audacity to translate the R^g-vEdam, totally forgetting the fact that at the mantRa level — higher than poetry and EVEN music — it is a sacrilege to TRANSLATE a mantRa and is totally wrong logically. In music, for instance, can we separate the sound from the emotional/aesthetic content? Indians seem to be believing more and more that this kind of integrals — words, poetry, music, mantRA-s — can be separated.
Where and when did we start falling into this foolish error?
DKM Kartha
sreenivasaraos
May 14, 2017 at 4:01 pm
Dear Shri Kartha
You are very welcome Sir. Yes; the point you made is very valid. Even from its early stages, the Sanskrit poetics has recognized the close association between the word and its sound, and between speech (vak) and meaning (artha).
The practice of disassociating word, it’s meaning from its sound seems to have come into being with the poets trying to be innovative in a very ‘clever way’.
Please see paragraph 3.1 of my post Chitrakavya – Chitrabandha
And also my post on Vakrokthi – Kavya and Indian Poetics – Part Nine
At some stage in the court-poetry, when the poets had to depend on Royal patronage, the body of poetry (Kavya-sarira) was made more alluring than its soul (Kavyasya atma).
The word-play (pada-jala) became rather prominent in the poet’s repertoire with clever use of alliteration of letters (anuprasa); alliteration of words (pada prasa), ambiguous use of a word where it conveys different meanings depending upon the context (latanu-prasa), play of pun (slesha or sabda slesha), change of voice (kaku) , and poetic subversion or deviant expression (vakrokthi) etc.
And, in the class of Chitrakavya (‘marvel poetry’) deliberate attempts were made to create ingenious and unusual forms of poetic compositions. The skilful artistry of words and dexterous enterprise of the poet ; clever arrangement of letters; different combination of words to evoke varied meanings where the sequence of words when read from the reverse direction –right to left produce a different meaning; and creating patterns based on the sound of the word rather than its meaning seemed to amuse the smart ones.
But, such sort of poetry was not accorded a high position (Adhama-kavya).
Perhaps the over-use of such artificial display contributed to decay and disappearance of the Kavya.
*
As regards music , its elements – Svara, Taala and Pada (words)- have hierarchical position , depending upon the type of music that is played. Please see paragraphs 4.2- 4.3 of Gandharva or Marga Music- Music of India – a brief outline – Part Six*
*
In Mantra, of course, the purity of the word , sound and intonation are very vital
*
Please do read my series on Kavya and Indian Poetics and also on Music of India – a brief outline
Regards
prathibha nandakumar
July 2, 2018 at 1:36 pm
Thank you again
sreenivasaraos
July 2, 2018 at 2:25 pm
Dear prathibha
you are welcome
Please do read the articles on other subjects too
Regards
Raj T
March 30, 2019 at 9:54 am
Namaskar
Many thanks for an Excellent , highly scholarly explanation and the best seen-
I am a student of Vedanta for 40 years and inc Shree Lalita Sahasranama-
your explanation of Vaak shakti in the four aspects is most beautifully explained.
I share this-• In the Srimad Bhagavad Gita Chp 10 Sl 10, 11, 22, 33, 34 and
in particular Sl 33, refers to the feminine qualities of” Kirtih, Shree, Vak ca narinam, Smrtir, Medha & Kashama viz. Fame, Fortune, Speech, Memory & Intelligence with Forbearance & Forgiveness,
She is described as:
Vagdevi – Goddess of Speech
Jihvagravasni – Dwelling at the tip of the tongue
Kavijih Vagravasini – Dwelling on the tongue of Poets
Shabdavasini – She who dwells in Sound
Vagisha – Mistress of Speech
Mahavani – Of great wisdom in Speech
Smriti-Sakti – Power of Memory
Jnana-Sakti – Power of Knowledge
Buddhi Sakti Swarupini – Whose form is the Power of Intellect
Kalpana Sakti – Who is the Power of Forming ideas.
Pratibha Sakti – Intelligence
Veda Garbha – the womb-source of Vedas Knowledge.
Sarva Vidya Swarupini – All forms of Knowledge
Sarva Sastravasini – Dwelling in the Shastras (Books of Shastra)
Granthakarini – Who creates the Books.
Mother Shree Saraswati represents INSPIRATION
Refer Nature of Inspiration (page 3) as in “Sarasvati” by R.L. Kashyap, Bangalore.
Also Sri Aurobindo’s description of Inspiration in this publication.
Namavalli No 1 : Om Sri Matre Namah
Salutations to the Divine Mother, who is the Mother of all.
Regards
Thank you sincerely
CaptTR Retd Chennai
sreenivasaraos
March 31, 2019 at 4:13 am
Dear Capt Raj,
I am honored by your visit ; and, the appreciation.
Thank you very much Sir
I also thank you for providing the varied descriptions of Vac Devi
*
I request you to please red the article devoted mainly to Vac , in her various forms, at
As regards the four levels of speech, the discussion is carried further , According t
Abhinavagupta at
and according to
Bhartrhari at
*
Warm Regards
Karishma Sharma
November 18, 2019 at 12:33 pm
A well written and thorough post about the Sanskrit language,