MN Roy: brief outline of life-events and thoughts- Part 10
Tashkent mishap
After the Second World Congress of the Communist International, the revolution was to advance eastward; and, yet its heart was in Europe. Chicherian, the Soviet Commissioner for Foreign Affairs, told Roy that ‘the revolution must spread eastwards; a second front of the world revolution must be opened in Asia’. He assured Roy that the Soviets are prepared to promote and support his struggle, in every way, against the colonial oppressors. He also informed him that great deal of preparatory work had already been done by the Soviet embassy at Kabul.

Afghanistan, strategically situated along many trade and migration routes, and sitting at the the southern edge of the Russian empire and poised adjoining the North West Frontiers of India, has been , throughout the history , regarded as the gateway to India from the West. Over the centuries, all imperial powers have tried to take control of this Central Asian region to gain access to India.
By the time of 1920 , at which time Roy was in Russia, two Afghan wars had already been fought during the 19th Century ( 1839-42; and 1878-80) in which the British in India had fought to extend their control over Afghanistan to oppose Russian influence there.
Afghanistan had, thus, been the main prize in the Great game played between the British Empire and the Tsarist Russia, since Afghanistan bridged the Central Asia with British India. Afghanistan and the North West Frontiers of India had been the customary battle ground between the two Imperial powers.
In 1907, confronted with the common enemy, the Germany, the imperial powers of Russia and Britain suspended their squabbling and entered into an Anglo-Russian Entente, settling their rivalry in Central Asia and in Persia. And, Afghan region was placed within the British sphere of influence.
But, after the war and with the success of the October Revolution, the equations between the British and the new Communist Government in Russia were disturbed. And, the terms of relation between British Empire and the Bolshevik were altered.
And, in the meanwhile, the new Emir Amanullah Khan (1919-29) of Afghanistan who took power in Feb-Mar 1919 began to favor the reformist minded young Afghan movement. Within about two months of his becoming the Emir, Amanullah Khan , adopting a turbulent attitude, denounced the existing treaties with the British ; opened negotiations with Soviet Russia; and , called upon the Muslims in India to wage ‘holy war’ (Jihad) against the British rule.
Following a three week conflict, called Anglo-Afghan war, Amanullah Khan pleaded for peace with British. He entered into a peace agreement (Treaty-of-Rawalpindi-August-1919) with British, acknowledging the British authority over the tribal belt of NWF Province. British let Amanullah Khan rule Afghanistan; but cut all types of subsidies. The treaty was later amended in 1921.
Before signing the final document with the British, the Afghans had concluded a treaty of friendship with the new Bolshevik regime in the Soviet Union. Afghanistan thereby became one of the first states to recognize the Soviet government and a “special relationship” evolved between the two governments.
(That lasted until December 1979, when the Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan; and, that proved to be the death knell of USSR. And, that also gave birth to the dreaded terrorist organization, the Taliban.)
***
Although the British had won the Afghan War of 1919, its British Indian army was exhausted from the heavy demands of World War I; and, British relations with the local tribal troops had also collapsed. Six to seven hundred of the erstwhile Khyber Rifles chose to move away from British ; and, turn into soldiers of fortune.
With so many foot-loose-discharged solders wandering around the troubled areas, the Soviets saw a window of opportunity to recruit such restless elements, with a view to gaining control over the tribal regions of Central Asia.
Further, according to their calculations, an independent Afghanistan and an independent Persia had diminished the British influence in the area; and this crack in the wall was indeed an opening for a possible anti-British nationalist movement. That alluring prospect attracted Bolsheviks to Kabul, again.
After the conclusion of the Second World Congress of the Communist International, at the suggestion of Borodin, it appears, there was a move to appoint Roy as the Ambassador of USSR in Afghanistan. That was intended to give Roy a credible tactical lever and immunity from British police to carry out his revolutionary ventures against the British rule in India, from across the borders of India.
The grandiose plan of the ECCI (Executive Committee of the Communist International) ; and its Central Asiatic Bureau (CAB) was to support Amanullah and to raise an army of Indian liberation soldiers in Afghanistan. It was hoped, the discharged Khyber Rifle troops and the recruits from the Muslims in India and the anti-British Pathan tribes would join the fight against the British in India.
Roy estimated that the British Indian Army exhausted after the long and strenuous War would have no zeal or strength to withstand the attack by his rebel Liberation Army. And, it was fondly hoped that the rebel army would occupy territories of Northern India and set up a government there. The newly formed government would support Indian liberation movement. As the ECCI saw it, M N Roy would be the central figure of that grandiose scheme.
Roy again began seeing visions of carrying arms into India to fight the British rule; but, this time thorough the North West instead of the North East corner of India.
However, the proposal to send Roy as the Ambassador of USSR in Afghanistan did not materialize; because of the sudden change in the political situation in Afghanistan. Emir Amanullah of Afghanistan who was till then entertaining anti-British notions, suddenly turned pro-British. As a result, the splinter groups of Indian revolutionaries who had sought refuge in Afghanistan were asked to stop their anti-British activities and leave the country.
Though the Afghanistan plan fell through, the Soviet Foreign office had not altogether dropped the idea of using Roy for rising rebellion in the East. Roy was co-opted into a small bureau of five members, called Mali Bureau set up by the ECCI (Executive Committee of the Communist International) ; and , Roy was asked to get involved with the activities of its Central Asiatic Bureau (CAB) charged with the responsibility of for forming policies for the liberation of the oppressed people of the East. Roy was informed that two prominent Russian members of (CAB) – Sokolnikov and Safarov – were already stationed in Turkestan; and that Roy should take over as the Chief of the military operations to be launched from Tashkent.
According to the geophysics of the Soviet Foreign office, a blow struck at British in India would inflict a serious setback to British power in Asia; and inspire anti-imperialist revolts from Syria to China in the East. And, that would set the East ablaze.
***
In the mean time, the Khilafat movement, a Pan–Islamic political protest campaign launched by the Muslims in British India broke out. The attacks on Turkey by Italian (1911) and Balkan (1912-13) forces as also the defeat of Turkey in World War I had caused severe unrest in Turkey. That was worsened by the Treaty of Sevres which not only detached all non-Turkish regions from the empire but also gave parts of the Turkish homeland to Greece and other non-Muslim powers. This was viewed by the Muslims as an attack on Caliph the Sultan of Turkey who was also the religious head of worldwide Muslim community; and as an attack on Islam itself.
In a meeting held in Switzerland, the Pan-Islamic Khilafat leaders declared that England was the only serious common enemy of Islam and Bolsheviks. And, therefore the union between the two was inevitable.
In India, a campaign in defense of the Caliph was launched, led by the brothers Shaukat and Muhammad Alī and by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad. The leaders joined forces with Mahatma Gandhi’s non-cooperation movement for Indian freedom, in return for his support of the Khilafat movement.
[The movement ended in disaster. Gandhi unilaterally suspended the CD movement after the Chauri Chaura incident; and, Mustafa Kemal Ataturk, the new leader of Turkey, abolished the Khilafat as he thought it to be outdated and superstitious. Indian Muslims were doubly disappointed and the history of Hindu-Muslim partnership in fighting for India’s independence was never the same again. The Muslim disillusionment with Congress also sowed the seeds of partition and creation of Pakistan.
Alistair Phillip, who worked at British Army (2005-2010) writes:
“Many believe the Khilafat Movement (1919), a protest by Indian Muslims against Turkey’s abolition of the Caliph, religious leader of the Arab world, to be the first step towards India’s Partition. Gandhi spearheaded this movement; but, failed to realize that the Pan-Islamic idea cut at the very root of Indian nationality. What did the movement achieve?
“First, Muslim fanaticism secured a position of prestige in Indian politics; thereafter their religious loyalty took precedence over national loyalty.
Two, the Muslim population hitherto divided among various groups and political pulls now became a solid force.
Three, a new fanatic leadership riding on the crest of the Khilafat wave came to wield the reigns of the Muslim leadership.“‘
All those who wish to know the underlying thoughts behind Partition should read Dr. B R Ambedkar’s book Thoughts on Pakistan back to back. The blame lies with all sides ]
Many young Indian Muslims under the influence of Pan–Islamic had come to believe that it was their religious duty to refuse to live under the rule of an infidel who did not protect their religious rights ; and, they should go on Hijrat (emigrate) and launch a Jihad (holy war) against the infidel rulers. These Mujahirs (emigrants) had also participated in the ‘Provisional Government of India ‘set up in Kabul during 1915 by the revolutionary adventurer Raja Mahindra Pratap, Muhammad Ali, Rahamat Ali Zakaria .
**
A faint echo of the Khilafat movement reached Moscow to encourage the view that Pan–Islamic movement was a revolutionary force; and, as such should be welcomed and supported as an alley of the proletarian world revolution.
For Roy, the Tashkent Bureau of Comintern offered an opportunity to realize his fond dream of raising a liberation army to march against the British.
Roy, in his Mexico days, wrote how he had ‘learned to attach greater importance to intelligent understanding of the idea of revolution’ the propagation of which was’ more important than the arms’. But, now, he again went back to the assertion that: ‘India will never be able to free herself from English rule by the goodwill of those same rulers. The only method is bloody revolution, however desperate this appears in the present circumstances.
In the Central Asiatic Bureau (CAB) , at Moscow , Roy advocated a plan for organizing a liberation army on Soviet Turkistan and march with it against the British in India to free the country , using at the same time the support of the militant tribes of the North West Indian frontier .
Roy expected to raise a nucleus of Indian Liberation Army at Tashkent by imparting military training to Muslim Muhajirs who left India because of the British stand against the Caliphate of Turkey. This force was to be further strengthened by drawing recruits from the tribes of North West frontier regions of India. The army was then to march into India to occupy some Indian territory and set up Soviet Republic. The new Soviet Republic was to give a call to launch a revolution and also a socio-economic program to attract the Indian masses. Roy had estimated that the British power in India, after the War, would have grown weak and it would not be able to withstand attack from North West.
Lenin, surprisingly, allowed Roy to pursue his plan of leading a military expedition through Afghanistan to liberate India from the colonial British rule. Perhaps, Lenin meant to combine Roy’s plan to strengthen Pan-Islamic rebellion against British with his own strategies. Lenin, however, advised Roy to wait for Stalin’s opinion. But, Roy could meet Stalin only by about the summer of 1921, by which time it had all come to an end.
[ When Roy first met Stalin, the latter was a sick person , about to undergo a major surgery. As Roy walked into the presence of Stalin , he was accosted by a sharp question, almost rebuking him. Roy writes :
“So, you do not see the revolutionary significance of Pan-Islamism?” I was staggered by the directness of the question. On my protesting that I had not come to discuss politics with a dangerously sick man who was to undergo a major surgical operation the next day, he laughed and reverted to the point. I inquired how he knew of my opinion about Pan-Islamism. “From Ilyitch” (amongst his close associates, Lenin was so referred to).
In the first meeting with Stalin, I avoided joining issues. My object was to get a first hand measure of the man.
After fifteen or twenty minutes, the general exchange of views was interrupted by a secretary who entered the room to deliver a message from the Chief Surgeon of the Kremlin Hospital.
Borodin made a sign: we must go, Comrade Stalin required rest. The latter sat up to shake hands ; and, with the peculiar Stalin grin said: “We must meet again as soon as this operation business is over.”]
***
In the late 1920, Roy was despatched to Tashkent to organize the Indian Revolutionary Army. With him, he took two trains, each with twenty-seven wagons loaded with weapons, ammunition and military supplies; ten wagons of dismantled airplanes; and, a supply of gold coins, British Pound and Indian Rupees. He also brought with him the staff for a military training School.
With such elaborate plan and preparations, Roy reached Tashkent in Turkistan, in Oct 1920; and, immediately plunged into work.
***
But, in Tashkent, Roy had to contend with numerous practical difficulties in organizing a Communist movement in the East. It was not as easy as he had been talking very eloquently all along of establishing proletarian supremacy over national struggles.
He failed to recruit sizable number of Khilafat emigrants in Tashkent for receiving military training and ideological indoctrination. He had also to contend with competition from Abdur Rab who was also recruiting Indians for his own revolutionary group located in Soviet Turkistan. Later M P B T Acharya also reached Tashkent and joined Abdur Rab.
The young Muslims that Roy could recruit included a group of 15 college students from Lahore. They were zealots, mujahedeen, members of the Pan-Islamic Khilafat movement in India, who regarded the preservation of the Ottoman Empire and the temporal authority and spiritual leadership of the sultan to be essential to the unity and welfare of all Muslims.
In the summer of 1920, 18,000 of them had left India for Afghanistan, some of whom intended to travel to Turkey to join the army of Mustafa Kemal Pasha, organizer of the Turkish Nationalist Party. On their way some fifty of them were captured by Turkmen tribesmen in Afghanistan and then liberated by the Red Army. They were then taken to Tashkent. Many among them were amused at being designated “representatives of the Indian revolution” resisted political education; and drifted away. Only a small number of Muhajirs who were attracted by the staunch anti-Imperialism of the Bolshevik government as also by the idea of ending exploitation of the masses, became enthusiastic Communists and played an active role in the Communist activities , especially in maintaining links with Punjab Communists. Of these, the most important was Shaukat Usmani , who was to become a leading figure in the Indian Communist Party.
Another group of young Muslims that Roy could recruit were Muhajirs inspired by the Khilafat movement who left India to join the Hijrat Movement. They left India with the object of going to Turkey through Soviet Russia; but were ill-treated by Muslim Turkmen counter revolutionaries. Some of the Indian Mujahirs (emigrants) then joined Communists and fought the counter revolutionary Turkmen. They reached Tashkent in late 1920; and joined M N Roy’s Military school at Tashkent and later went with him to Moscow.
Roy was not successful in smuggling arms and ammunitions to the Indian rebel groups and Mujahedeen in India , because the new regime in Afghanistan was no longer co-operating with Moscow ; and, also because the North West Frontier regions were heavily patrolled by the Indian Army.
Roy also did not succeed in recruiting the religious minded Indian Mujahedeen. This had a sobering effect on Roy; and, it led him to reconsider his ideas about the dichotomy of the national and class movement.
**
Although Roy was not successful in his mission of raising a Liberation Army to attack British rule in India by crossing over the North-West frontier, he was able to influence some Indian Muhajirs to become communists.
As instructed by the Comintern and the Turkestan Bureau of Comintern, Roy then went about the task of establishing the Communist Party of India. Eventually, on 17 October 1920, at Tashkent in a meeting convened by M N Roy and presided over by MPBT Acharya, the communist Party of India (CPI) was launched.
Besides M. N. Roy who was the Convening Secretary, six others who took part in the foundation of the CPI and signed the document were: were : Mrs. Evelyn Trent (Roy’s wife); Abani Mukherji; Rosa Fitingov (Abani’s Russian wife), Mohammed Ali (Ahamad Hasan), Mohammed Shafiq Siddiqui and M.P.B.T Acharya . Abdur Rab did not join the Party.
The minutes of the meeting read:
“It adopted a resolution establishing the condition of three months’ probation period (as candidate member) for those persons who wished to join the party. Comrade Shafiq is elected as secretary. The Indian Communist Party adopts principles proclaimed by the Third International and undertakes to work out a program suited to the conditions in India.”
It was signed by MPBT Acharya as Chairman and M N Roy as Secretary.
On 15 December 1920, three candidate members who had completed a probation period of three months were accorded full membership of the party. The same meeting also elected a three-member Executive Committee with Roy, Shafiq and Acharya. The party was registered in Turkestan and recognized by the Comintern as a group with a consultative vote during the Third Congress of the International in 1921.
The letter dated December 20, 1920 addressed to the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Turkestan, said: “It is hereby testified that the Communist Party of India has been organized here in accordance with the participles of the Third International. The Indian Communist Party is working under the political guidance of the Turkestan Bureau of Comintern.”
Though the CPI was launched successfully, it was not a smooth sailing. Virendranath Chattopadyaya objected to Roy setting up CPI in Tashkent and demanded its dissolution of ‘Roy’s ‘party’. In the meanwhile, the smouldering mutual hatred between Roy and Acharya flared up. Acharya denounced Roy’s leadership and demanded his expulsion from the Party.
According to the minutes of this meeting of the Turkestan Bureau, Central Committee, Russian Communist Party and Bureau, Communist Party of India, dated December 31, 1920:
“The conflict took place between members of the Indian Revolutionary Committee, Comrades Roy and Acharya, on grounds of disagreement of question of methods of work among the Indian émigrés in Tashkent. Comrade Roy proposes to leave with the Revolutionary Committee the charge of the work outside the country (USSR) and entrust the work among émigrés inside the country to the Turk Bureau of the Comintern. In this way, Comrade Acharya, remaining in the revolutionary committee (Indian), has to conduct wide underground work and the question dividing the members of Revolutionary Committee, therefore, ceases to exist at the moment. Comrade Roy is ready to abide by the decisions which would be taken in the present meeting, and suggests that Comrade Acharya continue to stay in the Revolutionary Committee.
Comrade Acharya considers it necessary to remove Comrade Roy from the work in the Bureau of the Comintern and the Indian Revolutionary Committee as he has lost popularity among the Indians”.
Following their dispute, Roy and Acharya were asked by the Turk-Bureau of the Central Committee and the Communist Party of Turkistan, on 31 Dec 1920, to go to Moscow and resolve their disputes there.
Because of the internecine squabbling between rival groups, the CPI at Tashkent could not function effectively. And, it was considered more prudent to form a Communist Party on the Indian soil.
***
The formation of the CPI was followed by the establishment of an Indian Military Training School in Tashkent.
The Indian Military Training School at Tashkent in October 1920 lasted only a few months before it was disbanded in May 1921 along with the Central Asian Bureau of the Comintern. Following Roy’s departure from Tashkent and the winding up of the military school, its Indian trainees were sent to Moscow to study at the Communist University of the Toilers of the East. The task of directing revolutionary activities in Central Asia was transferred to the newly formed Eastern Commission of the ECCI in Moscow.

The Communist University of the Toilers of the East, known in Russian as Kommunisti Cheskii Universitet Trudiashchikhsia Vostoka (KUTV) was established on 21 April 1921, following a decree of the All Russian Central Executive Committee. The decree stipulated that the KUTV was to be located In Moscow and was to be under the jurisdiction of the Peoples Commissariat of Nationalities which was instructed with the organization and direction of the project. Speaking on the fourth anniversary of the Communist University, Stalin explained the purpose of the University as:
“There are two lines of activity at the University: one, the purpose of which is to train cadres competent to attend to the needs of the Soviet Republics of the East , and the other, the purpose of which to train cadres competent to attend to the revolutionary needs of the toiling masses of the colonies and dependent countries; hence , the two kinds of tasks that confront the University of Toilers of the East’.

It played an important role in the ideological and political education for the Indian émigrés transferred from the Military School in Tashkent. Many of them maintained contacts with Communist groups in India, helping them with money and materials. Of the about least twenty-one young Muhajir students at KUTV, ten tried to return to India with the object of forming a communist movement. On their way to India, they were arrested and tried in the Peshawar Conspiracy Case and convicted to various terms of rigorous imprisonment.
Some Muslim Indian revolutionaries trained in the Military School at Tashkent and in KUTV in Moscow did manage to slip into India by late 1922. The Government of India tightened censorship and increased surveillance over such émigré. Shaukat Usmani , who was who was acting as a courier between Roy in Europe and communists in India; and, secretly circulating in India Roy’s newspapers and other writings was arrested. The British Government at Delhi instructed the Provincial Governments that “prompt and definite steps must be taken to counter M. N. Roy’s organization and propaganda and to terminate the activities of his principal followers.” Nine of Roy’s followers were tried in the Peshawar conspiracy case in 1923. The next year, in the Cawnpore Bolshevik conspiracy case, additional members of the Indian Communist Party, including Usmani, were convicted of conspiracy to organize a revolution to overthrow British rule in India. A court of appeal found the notion of a conspiracy ‘absurd and unbelievable’; and, ’ in effect the scheme had never been a serious threat to the security of the state’ . Since the defendants had, however, acted, ‘in the most serious spirit ‘ their appeal was denied and the convictions were upheld.
With the trial and conviction of the cadres of the Indian Communist Party, the British effectively suppressed the little that had remained of the small, irresolute, and disorganized followers of Roy. The leadership of the Communist Party of India was effectively compromised, at least temporarily, and potential followers were discouraged and threatened. Within about two years from the formation of CPI at Tashkent, the Indian Communist Party was reduced to twenty members; and, the Bolshevik revolutionary initiative to rope in the Muslims of southwest Asia and India had evaporated and ended for all practical purposes.

By about April 1921, Roy was instructed by Kremlin to close down the military school in Tashkent; to wind up his revolutionary activities; and, to return to Moscow. And, NKVD, the secret Agency as also the law enforcement agency that executed the orders of Soviet Supreme, directed diplomatic personnel in Afghanistan to have nothing to do with revolutionary elements, and ordered embassy officers in Persia to cease temporarily all political activities and their work with secret agents.
The Tashkent misadventure was wound up pretty quickly and tamely. Roy’s dreams of raising a revolutionary army and to march into India confronting the British in battles and liberating India had all come to naught. Even his military training school was shut down. The only thing that entered into record books was the founding of the Communist Party of India in Tashkent. And, that riddled with controversies and acrimony was not a happy experience, either. After the founding of Communist Party in India, the bureau at Tashkent became a mere foreign-outpost. It never had any significance.
The failure of the Tashkent venture had a chastening effect on Roy. It sobered his exuberance. It also moderated his views about the national and revolutionary movement in India.
***
In May 1921, Roy was summoned to appear before a Commission formed under the Chairmanship of Sebald Justinus Rutgers, the Dutch Marxist theoretician and journalist. Among the members of the Commission were Borodin and August Thalheimer, who were close friends of Roy. And, Roy also had known Rutgers when both attended the congress arranged by the Comintern Bureau at Amsterdam during February 1920. The Commission was formed to look into the allegations made against the behavior of Roy, while in Tashkent, by his Party colleges.
The complainants included Virendranath Chattopadyaya, Bhupendranath Dutta, Birendranath Dasgupta, P S Khankoje, GAK Luhani and Nalini Gupta. Abdur Rahman, Agnes Smedly and MPBT Acharya also joined them.
The Commission advised both the parties to resolve their differences amicably. But, the meet turned ugly, with shouting, swearing and hurling abuses at each other. There is no clear report on the discussions that went on before the Commission. There are in fact three versions of the meet: one by Roy as narrated in his Memoirs; the second by Dutta in his book, Aparakashit Rajanitik Ithihas (un-published political history) ; and, the third , in the speech delivered by Virendranath Chattopadyaya during 1934.
The argument of Dutta and his group was that the various classes engaged in the struggle should work together for bringing about political revolution against foreign rule. Dutta was not averse to Communists. He in fact said that Communist must be a part of the national struggle; Communist party should be organized from the base level to establish socialism; and should cause revolution. When Borodin questioned Dutta: in what way you differ from Roy, Dutta replied ‘’ Roy does not want to co-operate with nationalists for building revolutionary movements in India. From where else will you get people except from nationalists?’
The dispute was between two groups of Indians; the Communist Party set up at Tashkent was also not working; and, the cause of the dispute appeared to be mainly mutual dislike. The issue was allowed to lapse; and was buried.
I think, the dispute between the two groups could have been easily resolved, but for the subjective issues. Had not Roy dogmatically stuck to his stand of rejecting nationalism, the Communists in India , at least during the first phase of the mass struggle for national liberation in the post-war period , perhaps, had a better chance of working along with the national , revolutionary liberation movements. That was unfortunate because following the success of the October Revolution there was tremendous goodwill and sympathy for Indian liberation struggle. And, there was also an objective basis for cooperation of the nationalists and communists. Had the two groups come together, the International Communist movement could, perhaps, have established working relationship with the Indian nationalists in the freedom struggle.

What was more interesting than the seven month long sordid episode which eventually failed and through out which Roy fumed, puffed and sweated in Tashkent, was the tactical drama that was being played between the premier diplomats in Kremlin and London. Roy, at that time, was unaware of any of those schemes and maneuvers.
The Bolsheviks inherited both the assets and liabilities of the Tsarist Empire. As geophysical assets, it received vast territories embracing the heart land of the Euro-Asian continent. But, it also took over a rapidly growing polyglot population, their poverty and an underdeveloped economy with almost no technology.
But the Bolshevik Government did not inherit the relations and influences that its predecessors had built over the years with major European powers like France and Germany. The Bolshevik country was essentially a poor, underdeveloped agrarian economy and alone in the modern diplomatic world of the affluent West, none of which was particularly sympathetic to the international communist movement. It badly needed to get out of that rut, develop into an industrial power, to secure recognition from foreign powers, and to wield a clout in international diplomacy. The Bolsheviks realized that the key to enter into that hallowed world of the rich and powerful was Britain which then was the most advanced industrial power having a global reach.
The other major concern of the Soviet leadership was to expand and to build an international Communist movement and to align it with mass-based working class organizations in Europe and nationalist movements in Asia. There was also the question of the survival of the socialist republics inherited from the former Russian Empire and insulate them from foreign influences and interventions.
The problem of its own survival within the capital encirclement also became one of the main concerns of the Communists.
To achieve these ends, the Soviet leadership sought to obtain the technology of the advanced industrial countries, to construct protective zones on the frontiers of the USSR made up of stable states independent of the great powers; and, to find a secure position for Soviet Russia within the capitalist world order.
During 1920-21, the Communists changed the orientation of the Soviet foreign policy. In the preceding years the communist leaders were excessively harping on world revolution. But by 1920 that exuberance gave way to realistic appraisal of the ground-realities, as it dawned on them that revolution would take much more work and a longer time than they anticipated.
In order to overcome famine and internal strife and confusions, as also to build its defenses it needed some breathing space and aid from capitalist countries. It became necessary for Bolsheviks to build bridges across the gulf that separated them from the West. The most effective way of linking up with the West was trade, which would be mutually beneficial.
Because of the need for foreign trade, a revised diplomatic approach was required. Gone was the drive to instigate world revolution ; its own survival and viability now became the priority. Lenin eagerly looked forward to the possibilities for forging peaceful coexistence and good relations with foreign powers, coupled with an expansion in trade.
Communists badly needed to a period of peaceful co-existence to build their strengths.
Lenin , in his speech on 23 November 1920 , said : our task is to maintain the existence of our isolated socialist republic, which is so much weaker than the capitalist enemies who surround it; to remove the opportunity for enemies to create an alliance among themselves for a struggle against us.
In the same speech, Lenin also said that it was essential to re-establish trade relations though a temporary one, to re-build and to gain a breathing space (peredyshka). The breathing space, as he explained, was a sort of strategic retreat.
The aims of Soviet diplomacy in the 1920s were thus, to secure recognition from foreign powers, in order to emerge on the diplomatic scene as a fully accepted and functioning state equal to the world’s great powers, and to allow the Soviet Union the opportunity to develop economically by opening and maintaining channels for international trade. The extent to which Soviet diplomacy had to change and compromise its revolutionary aspects was central to the realignment of Soviet diplomacy during the 1920s.
***
It appears that the entire Tashkent expedition was played out to provoke, arm-twist and manipulate Britain to come to the negotiating table ; and to bargain in order to secure its aid for developing Russia’s infrastructure and industrial base; and, also to rehabilitate its sagging economy, to work out a pattern of close political co-operation. And that would secure for the Government born out of the October Revolution much needed stability, security, and technology; as also the conventional commercial and diplomatic relations with the governments of the capitalist states of Europe and with the authoritarian modern nations of Asia.
The British agencies were closely following the developments at the Second International Congress held in Moscow during July-August 1920. Its listening post in Copenhagen reported about the particular attention given to causing revolutions in Asia ; and said that ‘ a general revolt in the East next autumn was being planned in order to hurry up the World Revolution, for which the chiefs of Soviet Russia have great hopes’.
With heightening of the Soviet activities in Afghanistan and with its intense efforts to recruit Muslim rebels to build a revolutionary army to launch an assault on India, the British were very highly annoyed. Lord Curzon who then was the British Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs (1919–1924) was outraged and sent a strong protest to Moscow, vehemently objecting to the present aim and policy of Russia in Asia to encourage and build up hostility and anti-British propaganda in Afghanistan and elsewhere. It objected to Russian attempts to build centers of propaganda, a school at Tashkent and a powerful Muslim movement. All of which, Curzon pointed out, was clearly directed against British interests; and was intent on destroying the colonial base in the region, particularly in India. The Note concluded warning the Soviet Government of the serious consequences it will have to face because of its policy in Asia, to form a “powerful united Muslim movement to deal blow against the colonial base on which the Empire rests.
The Soviet Government offered to discuss the charges made against it, provided Britain was open to negotiate a trade deal with USSR. Lord Curzon who was earlier the Viceroy of India was fuming at Russian attempts to threaten British Empire in Asia. He was therefore reluctant to talk trade with the Bolsheviks. But David Lloyd the British Prime Minister and Winston Churchill persuaded him to take a positive look at the trade proposal and negotiate a deal with Russia , after prescribing stringent conditions safeguarding British interests in Asia.
Lloyd and Churchill advised Curzon that Britain which had just scrapped through the War was facing an unprecedented economic crisis: its industrial production was at its lowest; unemployment rates were soaring; its pre-war trade partners were in a similar rut; and, trade and economy was going down. They pointed out that the only industrial units working fulltime were the textile mills in Yorkshire; and, these were fulfilling Russian orders. And, if the proposal of trade negations does not go through it is very likely that the Russians might cancel their contract orders. Further, since trade agreement with Britain was vital to Russia, it surely would abide by conditions to be imposed in the trade agreement. Lloyd George, in short, advised that the way to alleviate postwar unemployment in England was through the restoration of pre-war world trade patterns. Since Russia’s trade with Britain would be mutually beneficial, Lord Curzon was advised to carry on the negations and finalize the agreement.
At the same time, Curzon was preoccupied with the Russian threat to the British Empire in Asia, and he and Churchill would agree to a trade treaty only as a way of ending revolutionary activity there. The two, therefore, would agree to a trade agreement only in case it ensured a counterrevolutionary strategy combining both’ détente and intransigence’ and promoting both foreign trade and imperial security.
After a series of long and protracted negotiations, the Anglo-Soviet Trade Agreement was finally signed in London on 16 March 1921. It was signed by Sir Robert Horne, Chancellor of Exchequer and Leonard Krasin, Peoples Commissar of Foreign Trade.
The significant paragraph from the preamble to the Trade agreement read:
‘That each party refrains from hostile action or undertakings against the other and from conducting outside of its own borders any official propaganda direct or indirect against the institutions of the British Empire or the Russian Soviet Republic respectively, and more particularly that the Russian Soviet Government refrains from any attempt by military or diplomatic or any other form of action or propaganda to encourage any of the peoples of Asia in any form of hostile action against British interests or the British Empire, especially in India and in the Independent State of Afghanistan. The British Government gives a similar particular undertaking to the Russian Soviet Government in respect of the countries which formed part of the former Russian Empire and which have now become independent.
[Trade Agreement between His Britannic Majesty’s Government and the Government of the Russian Socialist Federal Soviet Republic, Parliamentary Paper, 1921, cmd. 1207, pp.2-3]
David Lloyd the British Prime minister justified trade relations with Communist Russia calling it as ‘fighting the anarchy with abundance’. He said: Russia is necessary for recovery of Europe. Russia cannot be restored to sanity by force, as events have proved. Commerce has sobering effect as well as beneficial effects. The way to help Russia and Europe and Britain is by trade – that is to fight anarchy, wherever it appears, with abundance.
The Soviets in their turn justified the Anglo-Soviet Trade Agreement by describing it as : “ not an ordinary trade treaty with the mere object of regulating commercial operations between two countries; it was an agreement of politico-commercial character: it gave the RSFSR de-facto recognition by the most powerful capitalist power in Europe.”
The Soviets on their part promptly asked M N Roy to stop forthwith all rebellious activities harmful to British; disband all efforts to recruit Muslim mercenaries; shut down his military School in Tashkent; and, return to Moscow immediately. And, the NKVD directed diplomatic personnel in Afghanistan to have nothing to do with revolutionary elements, and ordered embassy officers in Persia to cease temporarily all political activities and work with secret agents.
After the conclusion of the Anglo-Afghan Treaty on 22 November 1921, the Russian consulates at Kandahar, Ghazni and Jalalabad were also closed down.
Most amazingly, in a note dated 27 September 1921 addressed to the British Government, the Soviet Government completely disassociated itself with the Tashkent mis-adventure. It said that a mischievous body posing itself Third International , made attempts to finance the propaganda school for training; and for equipping of sixty-two oriental students ; and, then for dispatching them to India to fight the British.
[Soviet Russia and the West, 1920-1927: A Documentary Survey by Xenia Joukoff Eudin, Harold Henry Fisher; Page 186]
Thus, despite the deliberations of the Second Comintern Congress, the rhetoric of Baku, and the plans made in the Small Bureau of the ECCI, the Bolshevik Government willingly bargained away support for revolutionary insurrection in Persia and India once it realized that support for revolutionary activity in Central and Southwest Asia was a strategic liability rather than an asset. It had also realized by then the prospects for proletarian revolution in Europe faded and anti-Communist regimes were consolidated there. It had also by then come to realize the folly and futility of supporting Muslim national and rebellious groups. In order to avoid such pitfalls and to establish and maintain normal relations with the leading nation of the capitalist world, the Soviets strategically gave up, at least temporarily, supporting revolutionary groups.
A fallout of the Anglo-Soviet Trade Agreement was that other European countries anxious not to miss out, not to be excluded from any trade agreements, lest they be left behind by other European powers, hurriedly entered into trade agreements with Soviet Russia. Western transportation experts came to Russia to help increase the efficiency of the old and overburdened railway system. And, the Western diplomats, expressing the new feeling of solidarity between their governments and Soviet Russia, co-operated with Russian efforts.
But, the western diplomats , however, did not spot the link between trade and diplomacy in quite the same way as the Soviets did.

In the months between Roy’s withdrawal from Tashkent and the Cawnpore Bolshevik conspiracy trial, Soviet foreign relations developed in other directions. In October 1921 the NKVD undertook a major initiative aimed at concluding a comprehensive postwar settlement of outstanding problems affecting Soviet relations with the victors of the World War – England and USA.
In April 1922 the Rapallo Agreement was signed, sealing the Soviet-German “special relationship” that would be the lodestar of Soviet diplomacy in the years to follow. It re-established normal relations between the Soviet Union and Germany. The two agreed to cancel all financial claims against each other; and, the treaty strengthened their economic and military ties. This was the first agreement concluded by Germany as an independent agent since World War I; and, that angered its Western Allies.
As Jacobson said: Lenin brought Soviet Russia into world politics in 1921 with a foreign policy conception composed largely of those of his pre-1917 ideas about the development of the early twentieth-century global political economy.
[For a more detailed analysis please see the lucid and interesting exposition by Jon Jacobson in his When the Soviet Union Entered World Politics . You may click the Introduction ; and then go down , to read the paragraph commencing with the lines : I argue that foreign relations were central to the political imagination of the Bolsheviks and to their actual political behavior from the day they came to power.
Please also read the Chapter : Conclusion , for more]

Continued
In
Next Part
Sources and References
When the Soviet Union Entered World Politics
When the Soviet Union Entered World Politics by Jon Jacobson
Soviet Russia and the West, 1920-1927: A Documentary Survey by Xenia Joukoff Eudin, Harold Henry Fisher
Communism and Nationalism in India: A Study in Inter-relationship, 1919-1947 by Shashi Bairat
Peasants in India’s Non-Violent Revolution: Practice and Theory by Mridula Mukherjee
In Search of Revolution: International Communist Parties in the “Third Period” edited by Matthew Worley
The Indian revolutionaries and the Bolsheviks – their early contacts, 1918-1922 by Arun Coomer Bose Top of Form
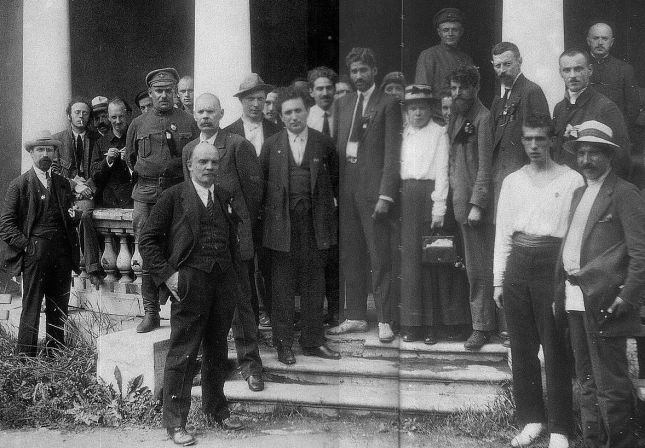
























 Michael Borodin, the Bolshevik leader whose original name was Mikhail Markovich Gruzenberg, born into a Jewish rabbinical family in Yanovichi, near Vitebsk in Byelorussia, in 1884, had joined the Bolsheviks in 1903. And, he became a close associate and follower of Vladimir Lenin in his various revolutionary activities. Borodin, besides being a revolutionary was an exceptional intellectual with wide experience. He had certain charm and sophistication about him. Borodin also possessed a striking physical appearance (he was, according to one description, ‘a man with shaggy black hair brushed back from his forehead, a Napoleonic beard, deep-set eyes, and a face like a mask’)
Michael Borodin, the Bolshevik leader whose original name was Mikhail Markovich Gruzenberg, born into a Jewish rabbinical family in Yanovichi, near Vitebsk in Byelorussia, in 1884, had joined the Bolsheviks in 1903. And, he became a close associate and follower of Vladimir Lenin in his various revolutionary activities. Borodin, besides being a revolutionary was an exceptional intellectual with wide experience. He had certain charm and sophistication about him. Borodin also possessed a striking physical appearance (he was, according to one description, ‘a man with shaggy black hair brushed back from his forehead, a Napoleonic beard, deep-set eyes, and a face like a mask’)




























 Sri Aurobindo 1908
Sri Aurobindo 1908
















 It was during his training period that Narendra Nath came to know Jatindranath Mukherjee (7 December 1879 – 10 September 1915) , fondly called Bagha Jatin (Tiger Jatin – as he was said to have killed a tiger in close combat). He was the principal leader of the Jugantar , the central association of revolutionaries fighting the British rule in India. He was at that time working as a shorthand clerk in the office of Finance Secretary, Bengal Government. But, Jatin was deeply involved in the revolutionary movement. He was affectionate by nature; had an attractive personality and could make friends easily. He gathered around him number of young and enthusiastic revolutionaries. Naren , who also was drawn to Jatin, came to like him immensely; and, he accepted Jatin as his leader. Later, the two worked together in a number of revolutionary ventures.
It was during his training period that Narendra Nath came to know Jatindranath Mukherjee (7 December 1879 – 10 September 1915) , fondly called Bagha Jatin (Tiger Jatin – as he was said to have killed a tiger in close combat). He was the principal leader of the Jugantar , the central association of revolutionaries fighting the British rule in India. He was at that time working as a shorthand clerk in the office of Finance Secretary, Bengal Government. But, Jatin was deeply involved in the revolutionary movement. He was affectionate by nature; had an attractive personality and could make friends easily. He gathered around him number of young and enthusiastic revolutionaries. Naren , who also was drawn to Jatin, came to like him immensely; and, he accepted Jatin as his leader. Later, the two worked together in a number of revolutionary ventures. 






 In the meanwhile, Barin Ghosh (younger brother of Aurobindo Ghosh) , around 1906, began organizing volunteers in support of agitations to be carried out as a part of the Freedom movement . His efforts drew those youth who were highly motivated and fired by the desire to secure Indian independence. The volunteers were trained in physical exercise, sword and lathi play; and were instilled with devotion towards the Mother land.
In the meanwhile, Barin Ghosh (younger brother of Aurobindo Ghosh) , around 1906, began organizing volunteers in support of agitations to be carried out as a part of the Freedom movement . His efforts drew those youth who were highly motivated and fired by the desire to secure Indian independence. The volunteers were trained in physical exercise, sword and lathi play; and were instilled with devotion towards the Mother land.


 The bomb used by the young Kudhiram Bose at Muzaffarpur was traced to the
The bomb used by the young Kudhiram Bose at Muzaffarpur was traced to the